Fractures in the lower leg can occur along the shaft of the tibia (shin bone), along the shaft of the fibula (smaller long bone) or both. The majority of tibia/fibula fractures are caused by either a twisting force when the foot is fixed or as a result of direct blow or trauma. Fractures to the lower leg can be non displaced (bones are still in position) or displaced (out of position). Lower leg fractures can also be either closed fractures (where the skin is not broken by the fracture fragments) or open fractures (where the fracture fragments have broken through the skin).The skin and tissues that cover the front of the tibia and fibula is very thin and as a result of this, a significant number of fractures to the lower leg are open fractures.
Fractures of the lower leg cause a significant amount of pain and movement is extremely difficult. There will be considerable deformity at the site of the fracture as well as a large amount of swelling and discolouration due to the amount of tissue damage and loss of blood at the fracture site.
Treatment of lower leg fractures can vary depending on the severity of the fracture. If the bone is still in its correct alignment (non-displaced) then immobilisation with use of a splint or cast followed by physiotherapy is recommended. In severe cases where the bone is displaced and the fracture fragments have broken the skin (open fracture) then external fixation is the appropriate surgery If the fracture is out of position (displaced) but the skin is still intact (closed fracture) then ORIF of the tibia and fibula (open reduction internal fixation) is required.
ORIF surgery is performed in an operating room, normally under general anaesthesia. During ORIF to the lower leg, an incision is made over the area of the fracture. The fractured bones are then realigned (open reduction) and held in place with a combination of pins, screws, and / or wires (internal fixation). The wound is then closed up using stitches or sutures. The pins / screws may remain in place permanently or they could be taken out at a much later stage. It is important to undergo ORIF immediately after suffering a displaced fracture of the lower leg as this will reduce pain, prevent deformities, aid the healing process and prevent further problems in the future.
Physiotherapy is imperative once the fracture site has healed sufficiently as this will maximise the success of the ORIF surgery and help ensure the return of full or near to full function in the lower leg.
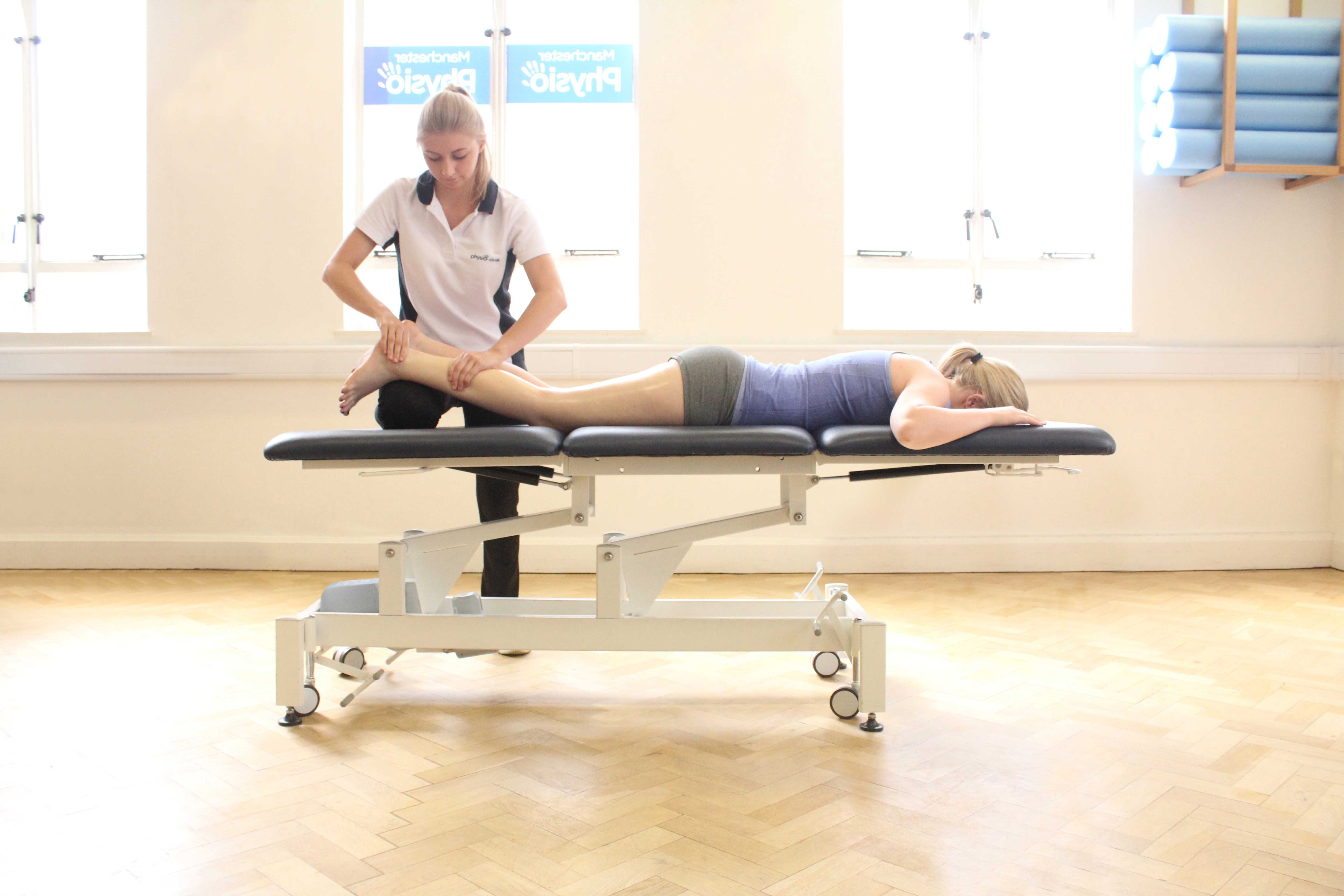 Above: Soft tissue massage of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles
Above: Soft tissue massage of the gastrocnemius and soleus musclesSymptoms after ORIF of tibia and fibula
Once you have undergone ORIF to the lower leg you will experience pain, swelling and decreased mobility in your affected leg. Elbow crutches will be provided in the initial stages of your recovery you will be unable to weight bear however progression to partial and full weight bearing is encouraged as soon as possible. The bones in the lower leg can take between 8 and 12 weeks to heal. You will suffer a reduction in function and muscle control due to prolonged immobilisation of your leg. Physiotherapy should begin as soon as possible for a rapid and problem free recovery; however, you will be unable to take part in a full and intense physiotherapy programme until the fracture site has healed adequately. You will be unable to drive until you have full and painless function in your affected leg.
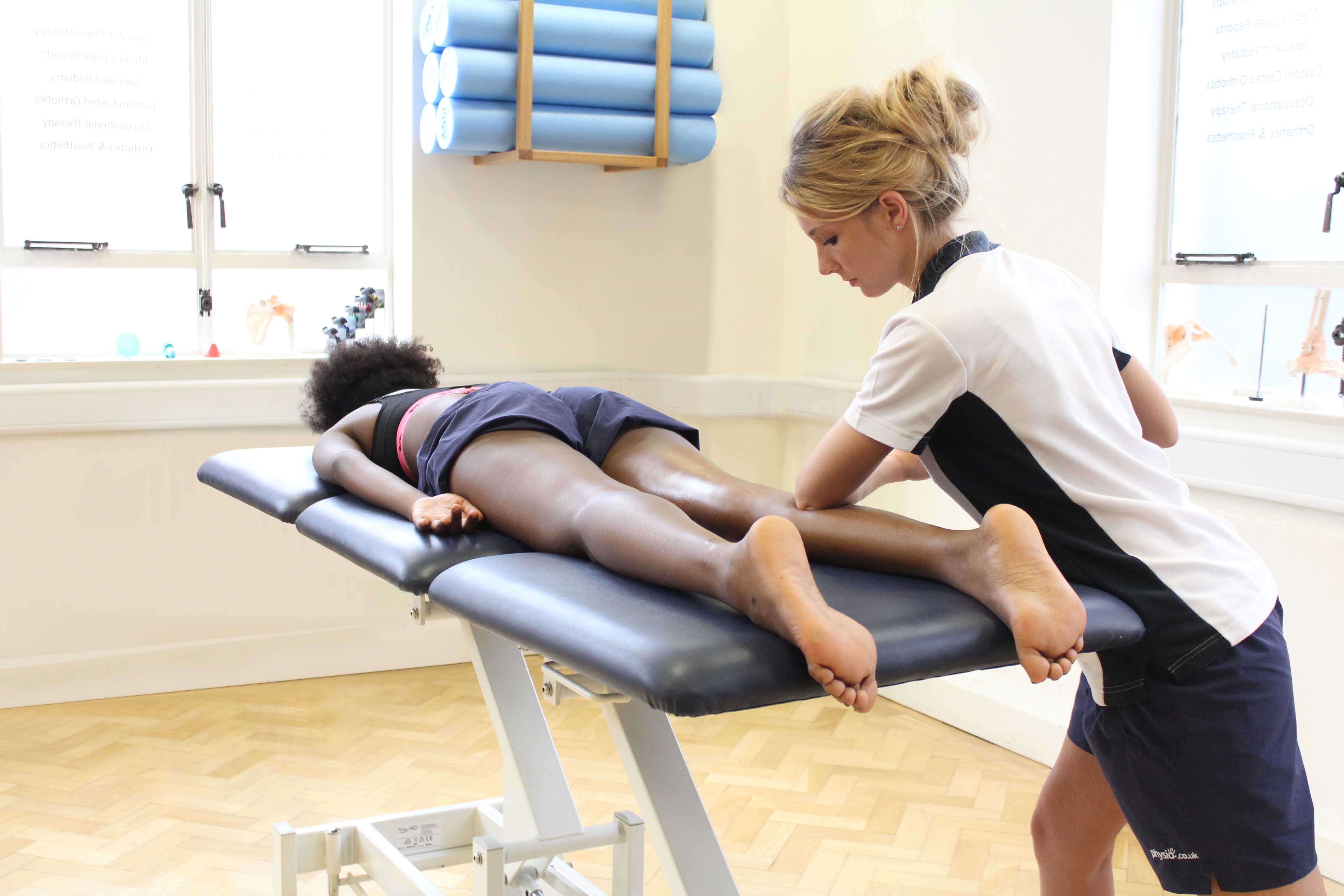 Above: Deep tissue massage of the gastrocnemius muscle
Above: Deep tissue massage of the gastrocnemius musclePhysiotherapy after ORIF of tibia and fibula
Physiotherapy is required as soon as possible once you have undergone ORIF surgery to reduce pain, stiffness and improve mobility, range of movement and strength in your affected leg. A comprehensive physiotherapy programme with Physio.co.uk will help you achieve the return of full or near to full function in your affected leg and also help prevent any future problems occurring. Rehabilitation can take up to 6 months after you have had ORIF surgery to your lower leg. Physio.co.uk offers a programme that includes goals that are personal to you. Goals include:
- To restore a pain free lower leg
- To restore full range of motion (ROM)
- To restore full muscle strength
- To restore full muscle length and flexibility
- To improve cardiovascular fitness and muscle endurance
- To re-establish independence
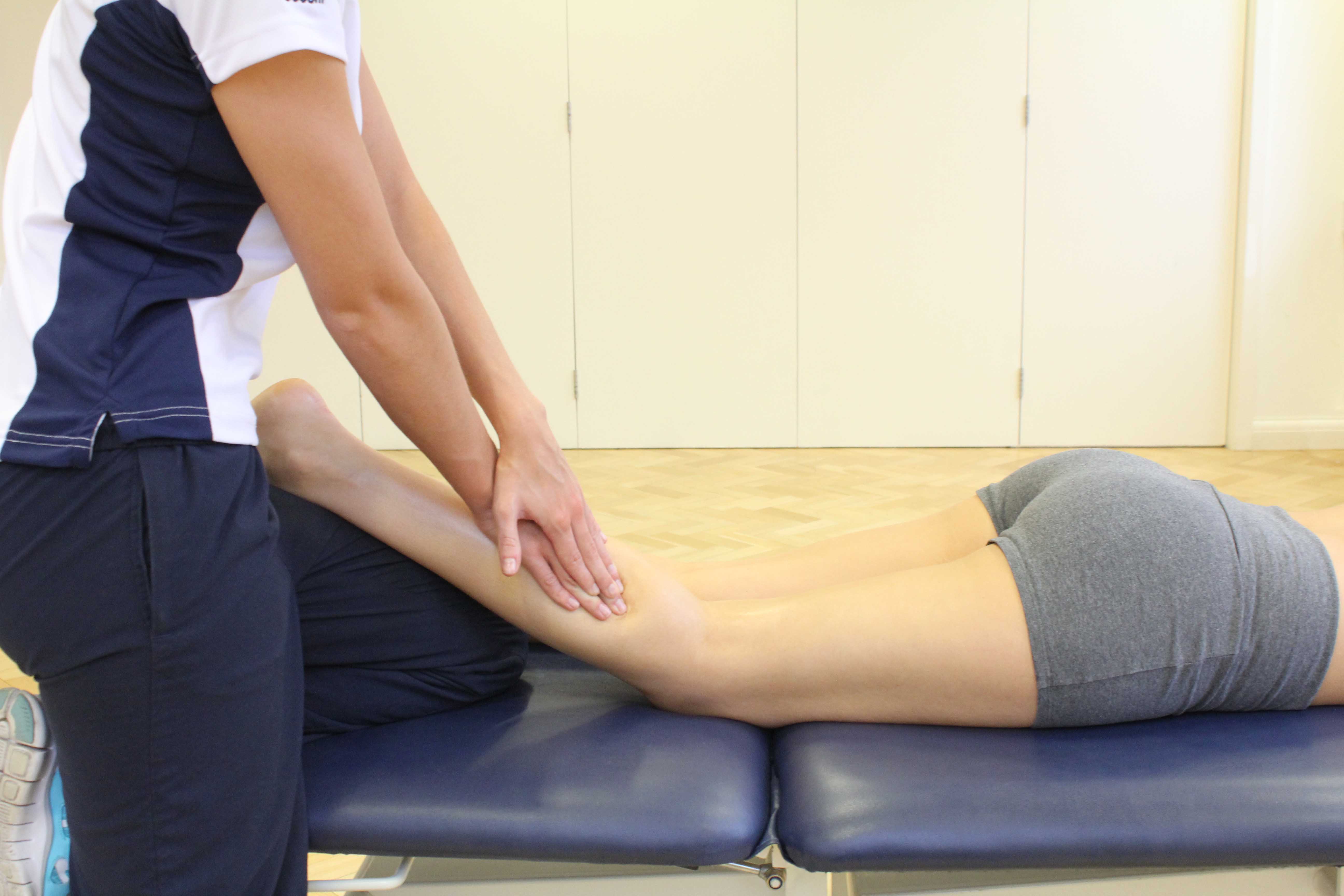 Above: Soft tissue massage of the gastrocnemius muscle by MSK therapist
Above: Soft tissue massage of the gastrocnemius muscle by MSK therapist0-4 weeks
During the first month of your physiotherapy programme with Physio.co.uk the main goals of your physiotherapy will be to reduce pain and swelling that you will be experiencing at this time. Your physiotherapy will aim to gradually introduce you back to gentle activity. Physio.co.uk will focus on maintaining the range of movement and strength in your affected and unaffected leg. Your physiotherapy will include:
- Pain killers (to control pain)
- Elevation (to control swelling)
- Crutch training
- Non weight bearing activities progressed to partial weight bearing activities
- Passive (assisted) range of movement exercises for affected leg (knee, ankle etc)
- Strengthening and range of movement exercises for unaffected leg
- Upper limb activities
 Above: Soft tissue massage of the gastrocnemius muscle by MSK therapist
Above: Soft tissue massage of the gastrocnemius muscle by MSK therapist5-8 weeks
During the second month of your rehabilitation with Physio.co.uk your physiotherapy will focus on the continuation and progression of activities from previous weeks. The goals of your rehabilitation include controlling pain and swelling, improving range of movement and flexibility along with increasing muscle strength and control. Your physiotherapy will aim to progress your ability to weight bear as much as possible at this time. Your physiotherapy will include:
- Continuation of modalities for pain and swelling
- Passive (assisted) and active (independent) range of movement exercises
- Strengthening exercises for muscles of affected leg (calf, hamstring, quadriceps etc)
- Stretching exercises for muscles of affected leg (calf, hamstring, quadricep etc)
- Range of movement, strengthening and stretching exercises for unaffected leg
- Progression of weight bearing – full weight bearing activities if possible
- Gait re-education training
- Proprioception and balance training
- Hip and ankle exercises
- Hydrotherapy
- Static bicycle
9-12 weeks
In the third month of your rehabilitation your physiotherapy programme will continue to focus on the progression from previous weeks. The main goals of your physiotherapy programme with Physio.co.uk will aim to minimise pain, improve range of movement, increase strength, re-train your gait and improve proprioception (balance). At this stage, your physiotherapy will also begin to include activities that will improve your cardiovascular fitness and muscle endurance. Your physiotherapy will include:
- Pain control
- Gait training (walking)
- Proprioception training (balance)
- Range of movement exercises
- Flexibility exercises
- Strengthening exercises for muscles in affected and unaffected leg (calf, hamstring, quadriceps, tibialis anterior etc)
- Hydrotherapy
- Static bicycle
3-6 months
Following three months of successful rehabilitation with Physio.co.uk you will have minimal if no pain and swelling. You will be fully weight bearing confidently and you will have seen marked improvements in the function of your lower leg. The main goals of your physiotherapy at this stage will continue to focus on the progression of exercises from previous weeks. Your physiotherapy will aim to improve the strength in the muscles of your lower leg by consistently building up resistance in the strengthening exercises. You should have full range of movement and your physiotherapy will aim to maintain and improve flexibility of both your lower limbs. Your rehabilitation will continue with proprioception and gait training. Cardiovascular activities such as hydrotherapy, cycling and gentle jogging can be included in your programme. Physio.co.uk will also include more functionally specific activities to promote independence.
The success of your recovery after open reduction and internal fixation surgery will highly depend on you commitment to your physiotherapy programme as well as the condition of your leg prior to the surgery. Recovery may take up to 6 months.
Summary
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) of the lower leg is a surgical procedure to treat a fractured tibia and fibula. Open reduction refers to open surgery to realign and set bone and is necessary for some fractures. Internal fixation refers to the fixation of screws and / or plates to enable or facilitate healing. ORIF surgery is necessary for a displaced (out of position) fracture of the tibia and / or fibula to stabilise and correct the injury. Is the fracture is non-displaced and the patella remains in position then immobilisation followed by a conservative (non-surgical) physiotherapy approach is recommended. ORIF surgery is crucial as this will reduce pain and prevent long term damage and loss of function in the affected limb. It is important to undergo a comprehensive physiotherapy programme after ORIF surgery as this will maximise the success of the surgery, reduce pain and stiffness, aid the healing process and improve mobility and function in the lower leg. A personal physiotherapy programme with Physio.co.uk will help you achieve the return of full or near to full function in your leg and get you back to what it is you love doing the most as soon as possible. Call Physio.co.uk now on 0330 088 7800 for more information or to book an appointment please contact us.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800