What is muscular dystrophy?
Muscular dystrophy is an inherited neuromuscular condition that progressively weakens the muscles in the body leading to reduced mobility.
Muscular dystrophy is caused by gene mutations that are responsible for the structure and function of muscles. The gene mutations change the muscle fibres, and interfere with their ability to contract.
Different types of MD affect different muscles. The severity of conditions, its clinical course and how it affects individuals varies greatly from person to person. Most conditions are progressive, causing the muscles to gradually weaken over time. Some people develop problems with their breathing and may need ventilatory support.
Some types of MD affect other body systems including the heart, gastrointestinal and nervous systems, endocrine glands, skin, eyes and other organs.
Physiotherapy treatment will help maintain muscle strength, flexibility, prevent joint stiffness and slow the physical progress of muscular dystrophy. Physiotherapy will also maximise a person’s potential and improve their quality of life.
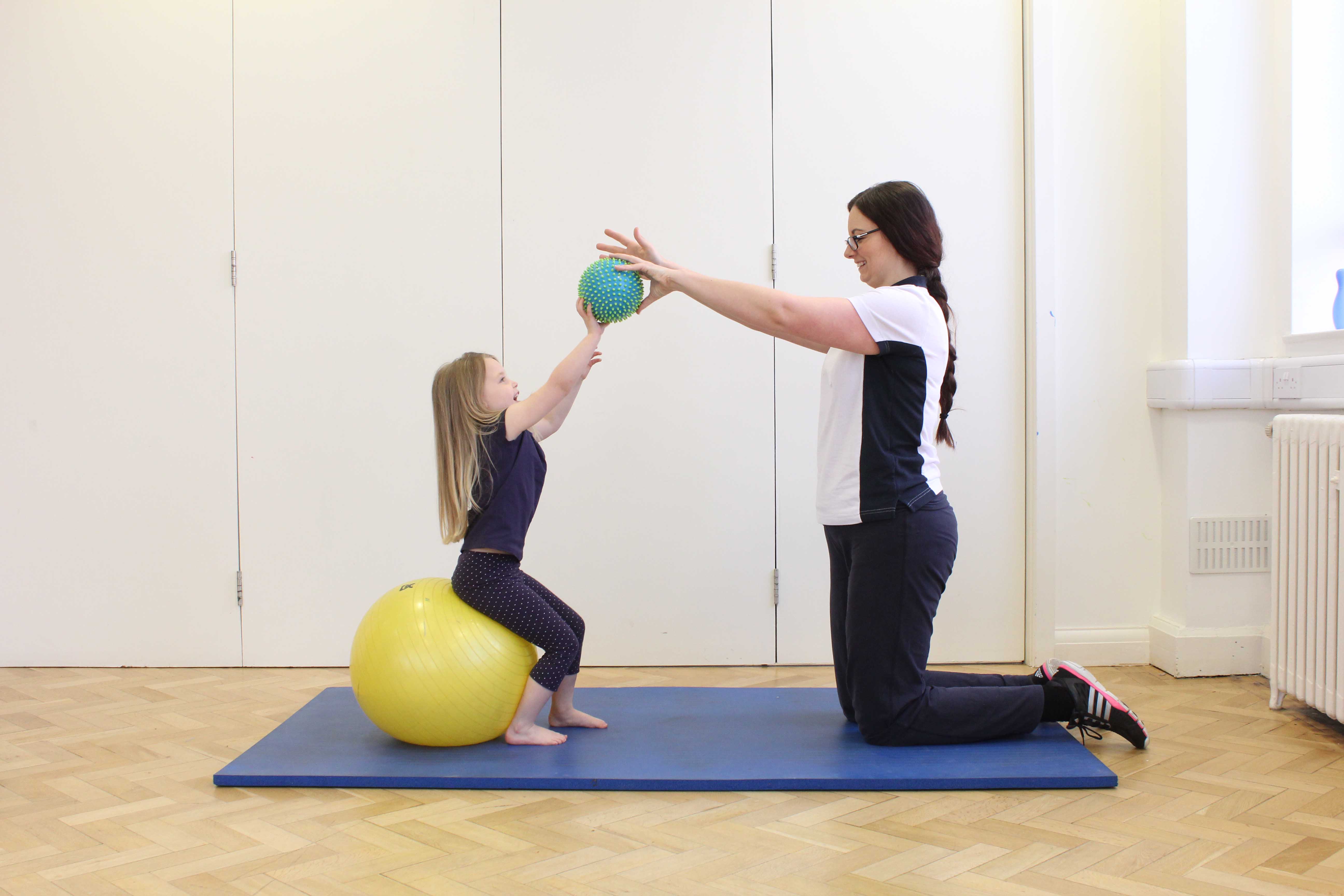 Above: Functional electrical stimulation used to facilitate normal dorsifexsion to improve mobility
Above: Functional electrical stimulation used to facilitate normal dorsifexsion to improve mobilityTypes of muscular dystrophy
There are many types of muscular dystrophy, some of the main types of muscular dystrophy are:
- Duchenne MD - The most common type of muscular dystrophy affecting more boys than girls. Duchenne MD is caused by a problem in the chromosome that codes for a protein called dytrophin leading to damage of the muscle cell wall.
- Becker MD – is a milder form of Duchenne MD affecting only males.
- Limb-girdle - causes weakness in the shoulder and pelvic girdle affecting the hip, thigh and shoulder muscles.
- Facioscapulohumeral - usually begins in the teenage years. It causes progressive weakness in muscles of the face, arms, legs, shoulders and chest. It can vary in severity.
- Oculopharyngeal - is characterized by late-onset (usually after the age of 45 years) causing eyelid drooping and swallowing difficulty.
- Myotonic dystrophy – the most common form in adults and causes prolonged muscle spasms, cataracts, cardiac abnormalities, and endocrine disturbances.
Diagnosis of muscular dystrophy
The diagnosis of muscular dystrophy is based on the results of a blood test or a muscle biopsyto see if there is muscle weakness that is typical of MD.
A detailed physical examination and the patient's medical history will help the doctor determine the type of muscular dystrophy. Specific muscle groups are affected by different types of muscular dystrophy.
The doctor may also observe a persons posture and gait as some types of MD cause a typical walking pattern.
What causes muscular dystrophy?
In most cases, muscular dystrophy is an inherited condition caused by a genetic mutation passed down through the family. This mutation in the gene alters the structure and function of muscles which can lead to a severe and progressive decline in mobility.
Occasionally, spontaneous gene mutations can cause muscular dystrophy to occur in people without a known family history of the condition.
What are the effects / symptoms of muscular dystrophy?
The effects, severity and onset of symptoms of MD are dependent on the type of MD a person has. The following symptoms may include:
- Progressive muscular wasting (weakness)
- Poor balance
- Frequent falls
- Clumsiness
- Difficulty walking
- Difficulty standing
- Difficulty climbing stairs
- Waddling gait
- Limited range of movement
- Breathing problems
- Drooping eyelids
- Back problems
Physiotherapy treatment will focus on controlling symptoms, such as muscle spasm and help keep your muscles working in as good a condition as possible. Physiotherapy treatment will include muscle exercises, because inactivity may make the condition worse.
Physiotherapy for muscular dystrophy?
At Physio.co.uk we understand that muscular dystrophy can have a significant impact on your life. Our dedicated physiotherapists at Physio.co.uk will help people with muscular dystrophy live more pain free and productive lives by maximising potential and promoting independence with everyday activities.
Physiotherapy treatment will help you maintain muscle strength and flexibility, and prevent joint stiffness as much as possible for as long as possible. Our specialised neurological physiotherapists will also provide support and advice on physical aids such as braces or wheelchairs to help maintain mobility. Physiotherapy treatment will aim to:
- Improve muscle endurance and muscle strength
- Improve balance
- Stretch and warm muscles
- Facilitate everyday activities such as walking
- Increasing fitness and energy levels
- Improve posture and reduce severity of back problems
- Improve mood
- Prevent joint stiffness
- Improve quality of life
- Promote independence
Our motivated neurological physiotherapists at Physio.co.uk will help keep your work, home and social life as active as possible whilst working within your potential. Physiotherapy treatment will include:
- Muscle training to improve strength in the muscles. Exercise will improve muscle endurance and muscle strength (prevent disuse atrophy) and help to improve mood. In the first six weeks of an exercise programme, the muscles will become more effective and efficient making everyday tasks easier.
- Stretching tight muscles to prevent contractures and ease muscle spasms. Stretching and strengthening will also minimise back problems.
- Correcting and varying position to increase comfort and prevent pressure sores.
- Exercise to increase stamina and reduce fatigue
- Activities to improve balance and make it easier for you to respond to differing surfaces such as slopes, hills, kerbs, gravel, and grass.
- Advice on mechanical support such as wheelchairs walking aids and orthotic devices in order to improve functional ability.
- Hydrotherapy and massage to relax sore muscles.
- Breathing control and assisted coughing if appropriate to maintain a clear chest.
To book an assessment call us on 0330 088 7800, book online or alternatively request a free phone consultation.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800