Causes of metabolic disorders
Metabolic disorders can be inherited from your parent’s genes or they can be acquired as an adult. Other medical conditions such as alcohol abuse, gout, kidney failure, pneumonia and sepsis can cause metabolic disorders. A family history of a genetic metabolic disorder or HIV/AIDS increases the risk of developing a metabolic disorder.
Types of metabolic disorder
Examples of metabolic disorders include diabetes, hereditary fructose intolerance, Gaucher’s disease, Niemann-Pick disease, Tay-Sachs disease and phenylketonuria.
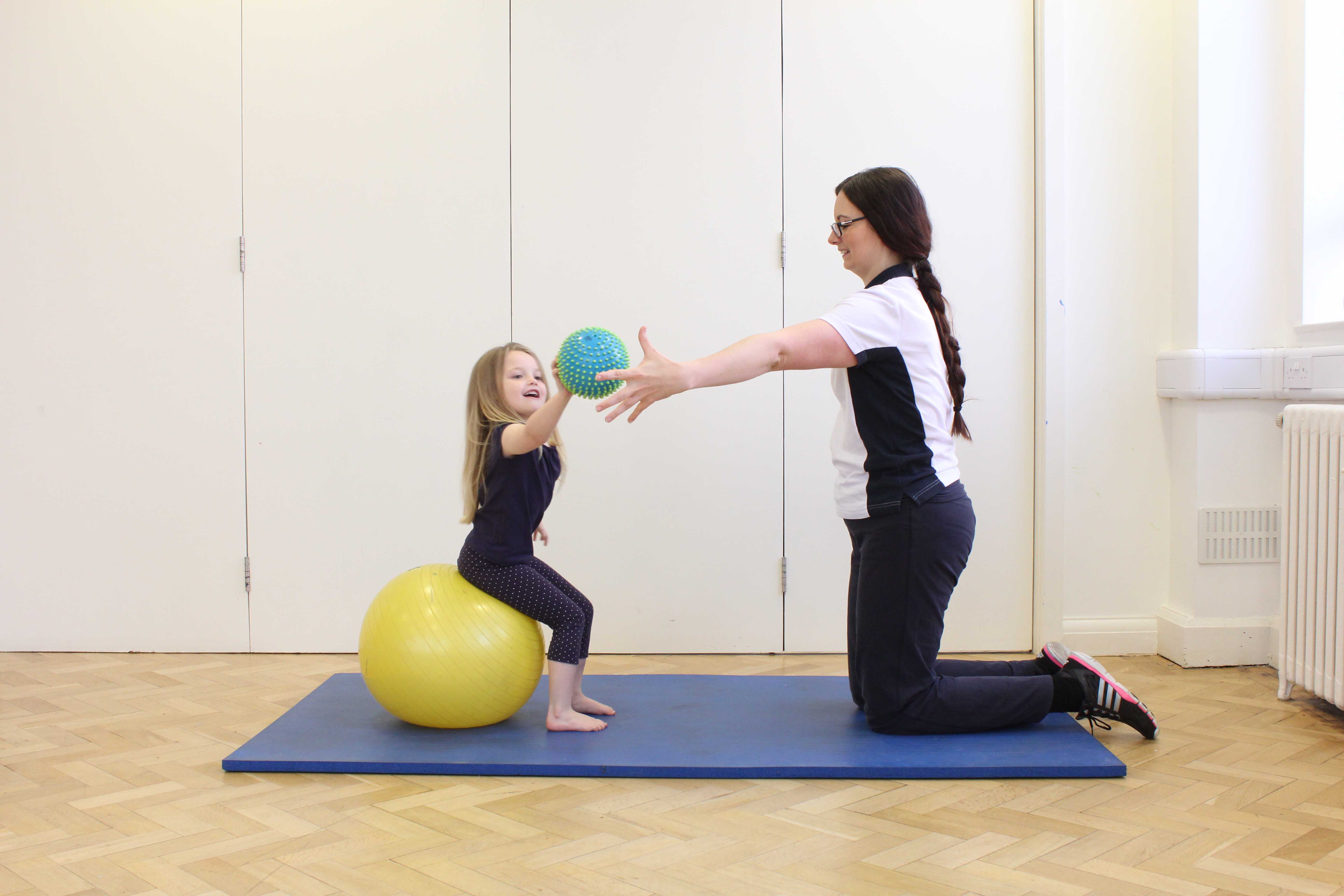 Above: Progressive strengthening and balance exercises to develop functional mobility, led by a paediatric physiotherapist
Above: Progressive strengthening and balance exercises to develop functional mobility, led by a paediatric physiotherapistSymptoms of metabolic disorder
The symptoms of metabolic disorder vary dependant on the type and the individual. As a result of an inherited metabolic disorder your child may experience a developmental delay both physically and cognitively. They may have difficulty thinking, speaking, writing and reading. This can make it very difficult for your child to communicate and learn. Children with metabolic disorders can have muscle weakness, twitching and spasms that can be minimised with appropriate physiotherapy treatment. Secondary to this condition, your child has an increased risk of infections and of thinning of the bones. It is essential that your child with a metabolic disorder receives holistic therapy from a multi-disciplinary team of specialists.
Treatment for metabolic disorders
Treatment for metabolic disorders begins by addressing the imbalance in chemicals in the body due to the disorder. Treatment options for your child include medication, vitamin and mineral supplements, counselling, dietary advice, surgery and physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy for metabolic disorders
Without medical treatment, metabolic disorders can potentially cause secondary complications such as organ failure, seizures, tremors and unconsciousness. It is important that your child maintains a healthy lifestyle with as much regular exercise as possible to avoid secondary problems. Following a thorough assessment, formulation of problem list and discussion of goals, a physiotherapy treatment plan may focus on:
- Monitoring of symptoms during exercise
- Promotion of cardiovascular exercise into daily routine
- Practice of moving around, transferring, walking, running
- Balance and co-ordination activities
- Core stability and muscle strength
- Stretches and positioning
- Assessment on use of walking aids, adaptations and equipment
An exercise plan will be provided for you to carry out at home on a regular basis with your child. The exercises will be dependent on the findings of the assessment and will be different for every child. Exercises for children with metabolic disorder may focus on fitness, muscle strength, balance, core stability and co-ordination. The exercises and treatment sessions will be fun but challenging in order to motivate your child and encourage participation and progress. Your child’s improvement will be monitored using a series of informal tests that will be repeated regularly to objectively demonstrate the benefits of physiotherapy. The benefits of physiotherapy are:
- Decreased risk of secondary complications
- Increased exercise tolerance and fitness
- Increased core stability, balance and strength
- Increased ability to move around and walk
- Increased independence and ability to carry out daily tasks
- Daily exercise as normal part of life
- Learn exercises to do at home in your own time
Why Physio.co.uk for metabolic disorders
At Physio.co.uk we understand that your child will have problems and difficulties due to the metabolic disorder. Our specialist physiotherapists are able to provide effective treatment and advice in order to ensure your child achieves and maintains the highest possible standard of living.
- Knowledgeable physiotherapists with experience with metabolic disorders
- Regular liaison with other health professionals involved in individuals care
- Treatment at any stage of your condition
- Treatment at home, in the clinic or gym
- Provision of aids, equipment and adaptations
- Provision of home exercise program
- Access to occupational therapy
- Access to specialist gymnasium

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800