Cellular exchange is where healthy oxygen and nutrients are provided to muscles as waste products and toxins are removed. A range of techniques can be used within a massage to increase cellular exchange. Increasing cellular exchange can help reduce swelling, pain and can speed up healing. Massage therapists at Physio.co.uk use increased cellular exchange through massage to help maintain healthy muscles and treat delayed onset muscle soreness.
What is increased cellular exchange?
Cellular exchange is the process in which waste products and toxins within muscles are exchanged for healthy nutrients and oxygen. When cellular exchange increases, muscles become healthier and stronger and are less likely to fatigue and weaken. Waste products and toxins are removed through the lymph flow. The lymph flow is part of the lymphatic system. Healthy nutrients and oxygen are brought to the muscles through blood flow which is part of blood circulation. A massage encourages an increase in blood circulation and stimulates the lymphatic system. Increasing the flow of blood and stimulation of the lymphatic system through massage increases cellular exchange.
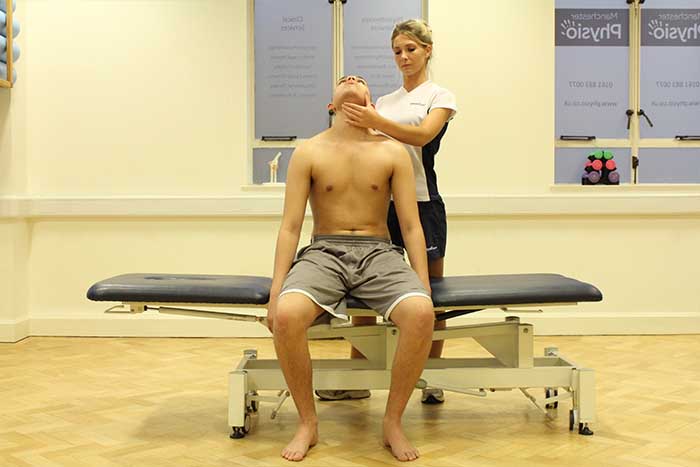
What are the benefits of increased cellular exchange?
There are a variety of benefits gained through increased cellular exchange. The common benefits gained through increasing cellular exchange include:
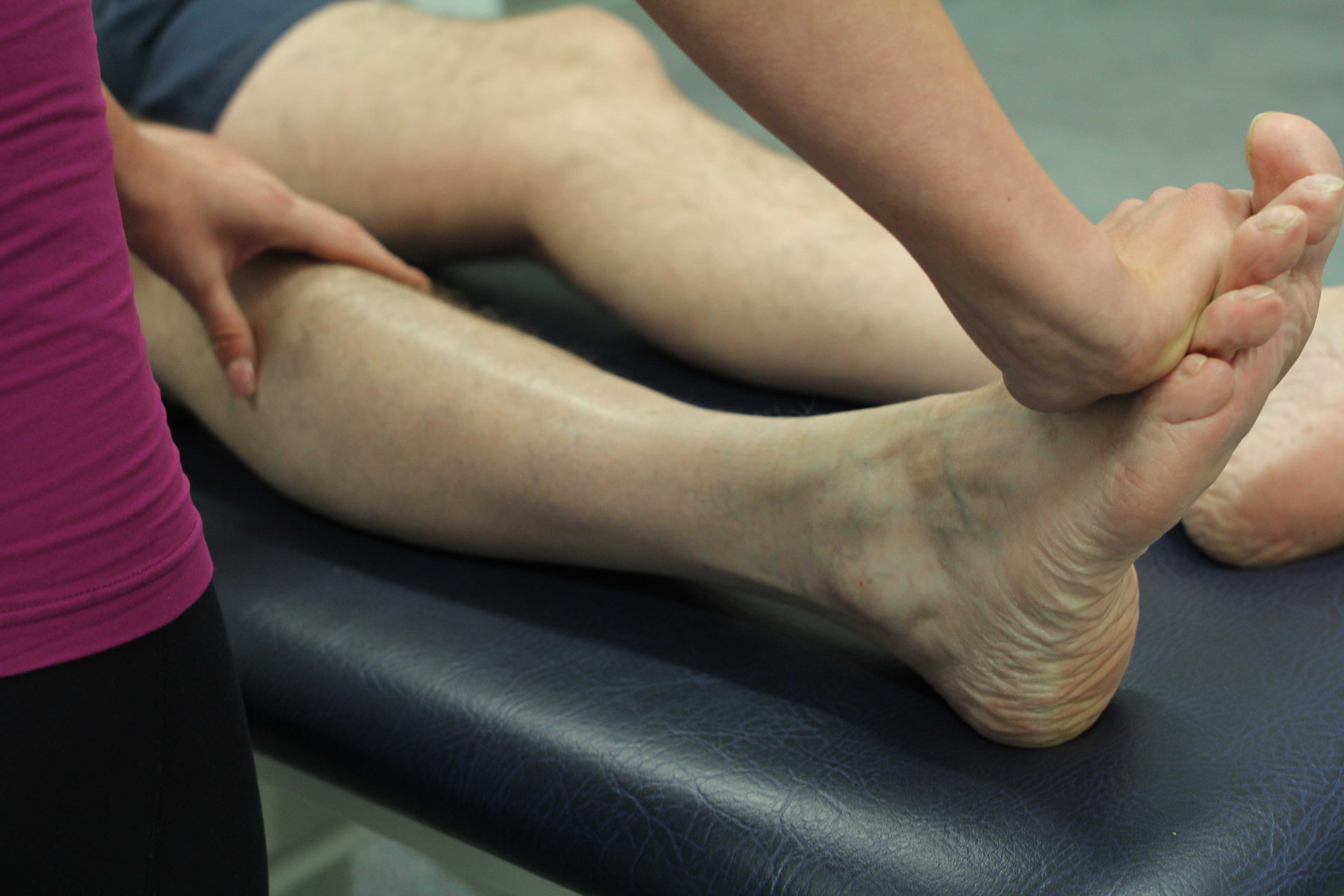 Above: Cellular exchange is the process of removing waste products and toxins.
Above: Cellular exchange is the process of removing waste products and toxins.Increased cellular exchange can maintain healthy muscles. Increased cellular exchange helps to remove waste products from within the muscles more efficiently. A build-up of waste products can cause muscles to fatigue and weaken. Waste products that are removed are exchanged with healthy nutrients and oxygen that help keep muscles strong and full of energy. Increasing cellular exchange therefore maintains healthy muscles.
Increased healing is a common benefit of increased cellular exchange. Common injuries include muscle pulls, tears and strains. During healing, there is a repair phase. This phase can often be slowed down if muscles are not provided with essential oxygen and nutrients. Essential oxygen and nutrients aid in the repair of muscles. Healing time can be further reduced when a build-up of metabolic wastes occur. Increasing cellular exchange helps to remove metabolic wastes and exchange them for the essential oxygen and nutrients. Healing time can then be reduced due to the increase in cellular exchange.
Increased cellular exchange can reduce swelling. There are many reasons swelling can occur. The most common reasons of swelling include injury and surgery. Swelling is a build-up of excess fluids and waste products. Swelling occurs to protect a site of injury from further damage but can however increase pain and restrict movement. When cellular exchange is increased, excess fluids and wastes products are removed from the injury site more efficiently. An increase in healthy oxygen and nutrients are also delivered to help repair any damaged tissue cells. Removing waste products and excess fluids from the injury site helps to decrease swelling.
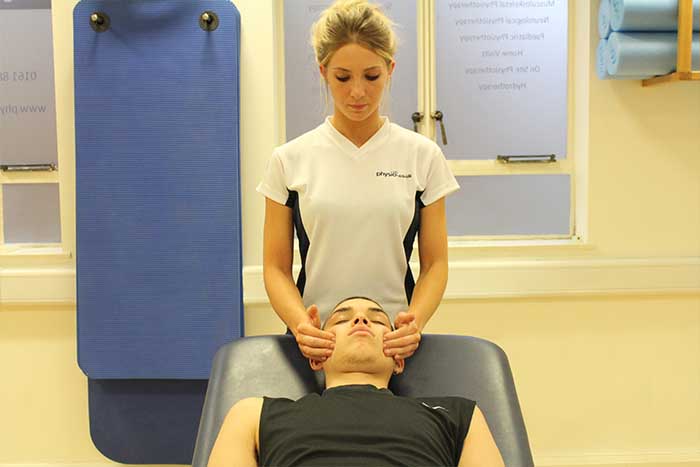
What techniques are used to increase cellular exchange?
A range of techniques can be used to increase cellular exchange. The most common techniques used to increase cellular exchange include:
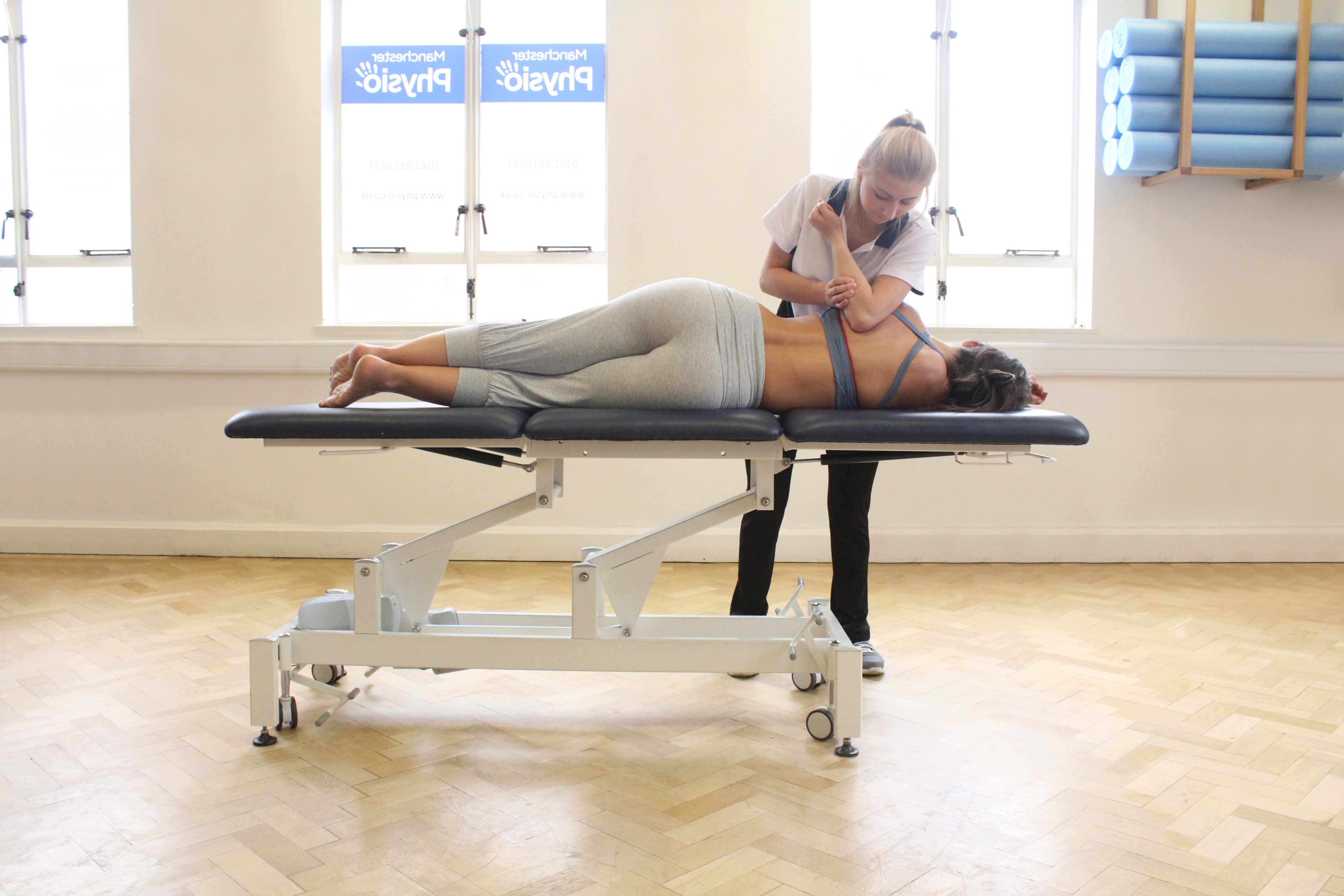 Above: Impoved cellular exchange can enhance recovery and reduce the onset of muscle soreness.
Above: Impoved cellular exchange can enhance recovery and reduce the onset of muscle soreness.Effleurage can be used to increase cellular exchange. Effleurage is performed using flattened hands and fingers. Effleurage can vary in pressure depending on the condition or to personal preference. The temperature of muscles increases when effleurage is performed as it encourages an increase in circulation. The encouragement of circulation increases cellular exchange as the lymphatic and blood circulation are both stimulated and increased.
Cellular exchange can be increased using trigger pointing. Trigger pointing is where thumbs or fingertips are placed on areas of the body containing tension or muscular knots and a firm pressure is applied. Trigger pointing helps to increase cellular exchange as circulation of the blood and lymphatic system are increased. Circulation is increased as an ischemic reaction occurs. An ischemic reaction is where blood flow is restricted when pressure is applied to the trigger points and is then increased as pressure is released. Trigger pointing helps to break down and soften muscular knots that can cause pain, tension and restriction.
Wringing is commonly used to increase cellular exchange. Cellular exchange, much like effleurage and trigger pointing, is increased as wringing encourages an increase in circulation. Wringing is performed using flat hands and fingers and is where soft tissues from either side of the treatment area are pulled to the centre in opposite directions. Wringing can decrease muscle tightness and tension whilst also being a relaxing experience for the person.
What situation would increased cellular exchange help?
Increased cellular exchange can help in a variety of ways. Ways increased cellular exchange can help include:
Increased cellular exchange can help treat delayed onset muscle soreness. Delayed onset muscle soreness is caused by microscopic tears within muscle fibres. Waste products such as lactic acid also contribute towards delayed onset muscle soreness as they increase muscular fatigue and pain. Increasing cellular exchange can help reduce pain caused by muscular fatigue. Cellular exchange aids in the removal of waste products through the lymph flow. Cellular exchange can also increase the healing of the microscopic tears by increasing the availability of oxygen and nutrients that help increase healing and reduce muscle weakness. Decreasing waste products and increasing oxygen and nutrients therefore helps decrease the effects of delayed onset muscle soreness.
Increased cellular exchange can help post event. Muscles may contain increased amounts of waste products post event. Leaving waste products within muscles can often lead to increased fatigue and also delayed onset muscle soreness. Cellular exchange helps to remove waste products before they can leave damaging effects on the muscles and increase muscle weakness and pain. Cellular exchange also provides muscles with an increase of healthy nutrients and oxygen that help to keep muscles strong which further reduces chances of delayed onset muscle soreness and muscular weakness and fatigue.
The effects of injury can be helped when cellular exchange increases. After an injury, effects such as swelling, pain and increased build-up of metabolic wastes may be left around the injury site. Increased swelling and a build-up of metabolic wastes can slow down healing and increase the damaging effects of injury. During a massage, cellular exchange is increased to exchange metabolic wastes with healthy nutrients more efficiently. Exchanging metabolic wastes for healthy nutrients helps to reduce swelling and decrease pain therefore reducing the effects of injury.
Summary
Increased cellular exchange is where waste products and toxins are replaced with oxygen and nutrients within muscles. There are many benefits of increased cellular exchange including the maintenance of healthy muscles, increased healing and reduced swelling. A variety of techniques can be used to increase cellular exchange. The most common techniques used include effleurage, trigger pointing and wringing. Increased cellular exchange can help treat many different conditions. Common conditions increased cellular exchange can help include delayed onset muscle soreness, post event and post injury. Our massage therapists at Physio.co.uk increase cellular exchange through massage to help reduce pain and decrease muscular fatigue.
How can I arrange a sports massage to increase cellular exchange?
The easiest way to arrange a sports massage to increase cellular exchange at Physio.co.uk is to email us at office@physio.co.uk or call us on 0800 033 7800.
Alternatively if you have any questions please feel free to contact us.
We offer a 7 day service and provide home and clinic appointments.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800