What is paediatric dyskinesia?
Dyskinesia in children is when the body makes jerky body movements. The movements are uncontrolled, purposeless, rapid motions which disrupt normal movement or posture.
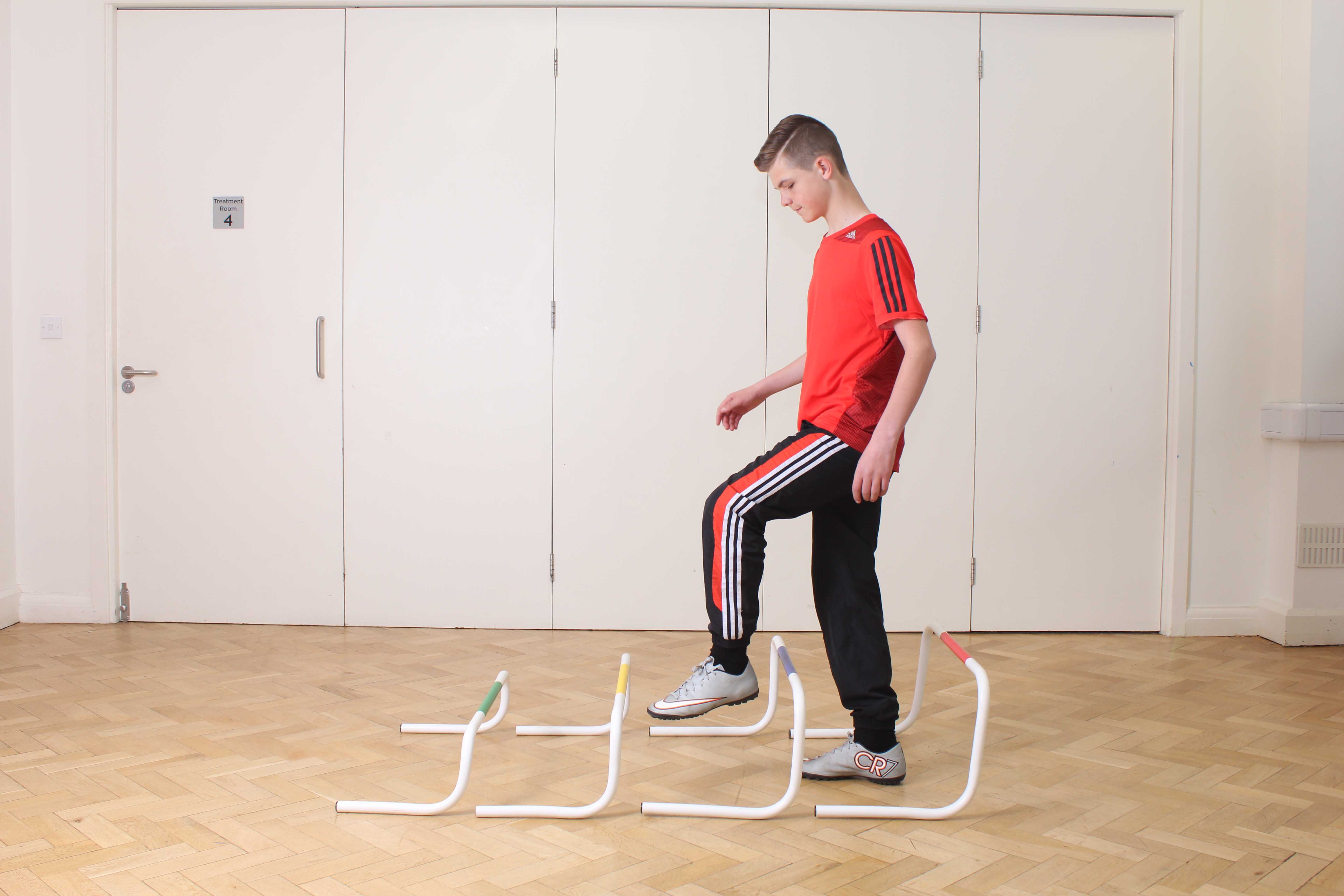 Above: Gross motor function exercises designed to improve co-ordinated movement
Above: Gross motor function exercises designed to improve co-ordinated movementWhat causes dyskinesia in children?
Jerky movements in children may occur due to:
- Impairment/damage to part(s) of the brain that control movement
- Abnormalities in brain chemicals. For example a reduction in dopamine levels can result in the transfer of messages from the brain to the muscle taking too long, or arriving in intermittent stages.
- Athetoid Cerebal Palsy
- Angelman Syndrome
- Wilson’s Disease
What types of dyskinesia movements are there in children?
There are several types of movements that can occur as a result of dyskinesia such as:
Chorea
Fast, non-rhythmic, uncontrolled jerky movements, mainly occurring in the arms and legs. Chorea also may affect the hands, feet, trunk, neck, and face.
Ballism
Like chorea, but the movements are much larger, more explosive and involve more of the arm or leg; it usually occurs due to a cerebrovascular event.
Myoclonus
A sudden, brief, jerky, shock-like involuntary muscle contraction. Myoclonic jerks may occur singly or repetitively. Unlike tics, myoclonus cannot be controlled even briefly.
Dystonia
Involuntary sustained or intermittent muscle contractions result in twisting and repetitive movements, abnormal postures, or both. Dystonia gives a rhythmic appearance to the movement, or may be unrelenting to provide a fixed posture.
Tics
Repetitive stereotyped movement. Patient can initiate voluntarily and can also intentionally suppress for a short time.
What are the symptoms of dyskinesia in children?
There are several symptoms that a child with dyskinesia may show, such as:
- Facial grimacing
- Lowering and raising the shoulders
- Extending and bending the fingers and toes
- Child may appear restless or jittery
- Jerky or uncoordinated movements when performing activities
What can physiotherapy do to help children with dyskinesia?
Physiotherapy treatment can help children with jerky movements. Passive movements of joints can help to maintain movement in the child’s limbs so that movement becomes easier. Exercises are used so that the child can improve control over their limbs. These exercises can then be progressed onto practising normal movement patterns so that functional movements become easier to achieve.
Summary
Dyskinesia is the term used for jerky movements which are uncontrolled, rapid movements which disrupt normal movement and posture. They can occur due to damage to the brain, as well as abnormalities in brain chemicals. There are different types of jerks including Myoclonic jerks, Chorea, Ballism, and Dystonia. Children having problems with jerky movements may present with facial grimacing, uncoordinated, rhythmic movements, jerky movements, or extending and bending their fingers and toes. Physiotherapists at Physio.co.uk can help, through maintaining joint range of movement, and normalising movement patterns.
To book an appointment or for more information about paediatric dyskinesia contact us or call 0330 088 7800.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800