Massage has been used widely as a healing method for many years and is considered an effective treatment and management strategy for individuals suffering from neurological disorders by targeting common symptoms. An individual with a neurological disorder may experience a reduction in flexibility, range of movement and an increase in pain, stress and muscular tightness. The therapists at physio.co.uk can use and adapt a wide variety of massage techniques to suit the individuals needs and treatment goals.
What is massage for neurological disorders?
Neurological disorders are diseases that affect the brain, spine and the spinal nerves that connect them. There are over 600 known neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease, stroke, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis and cerebral palsy. Symptoms associated with neurological disorders include a reduction in flexibility, range of movement and an increase in pain, muscular spasm and tight muscles. Many symptoms associated with neurological disorders can be addressed through massage therapy which can enable the individual to gain a greater quality of life.
When can massage help for neurological disorders?
Massage therapy can be used in conjunction with conventional treatment to manage multiple symptoms of neurological disorders. Massage treatment when applied in certain situations can be extremely beneficial such as;
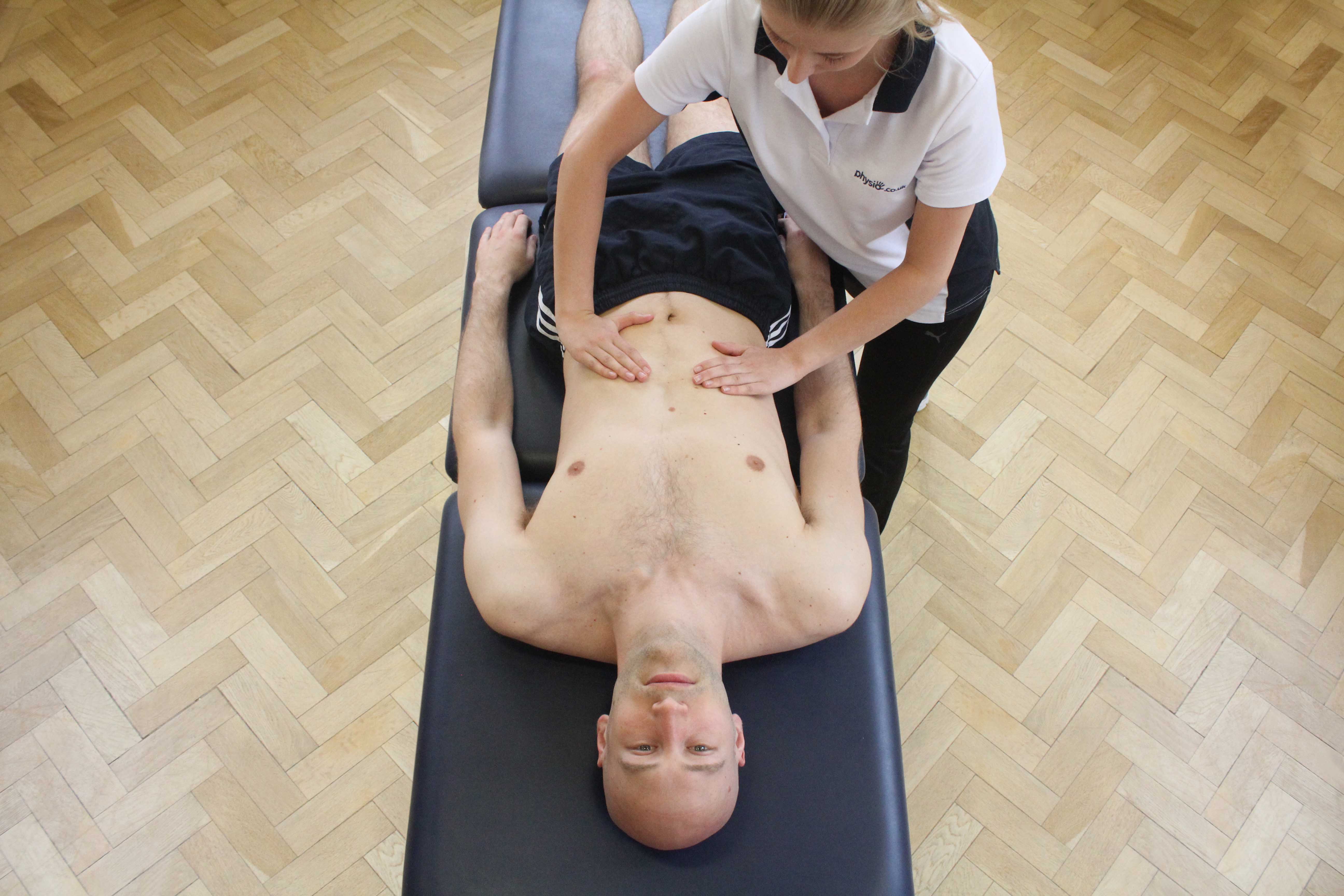 Above: soft tissue massage of the abdominal muscles by a specilaist massage therapist
Above: soft tissue massage of the abdominal muscles by a specilaist massage therapistMassage when applied to an individual suffering chronic pain can be extremely beneficial as the individual is able to feel a significant reduction in pain immediately. Chronic pain is often associated with neurological disorders with many individuals believing there is no hope to reduce chronic pain. Massage can promote a sudden reduction in pain through a process known as the pain gate theory whereby impulses sent to the brain regarding the painful stimulus are blocked by impulses regarding non-harmful stimulus such as massage.
Massage can be extremely beneficial to an individual experiencing high muscle tone alongside their neurological disorder. High muscle tone is associated with neurological disorders due to the effects on brain activity and its effects on muscular contractions and reflexes. Massage therapy can help relax the muscles which have high tone such as the wrist flexor muscles during cerebral palsy. Massage can reduce muscle tone by initially warming the tissue up through friction and increasing blood circulation through vasodilation. Massage can then use deep and stretching strokes to elongate the tight adhesive muscle fibres to allow for improved tissue flexibility.
Massage can be extremely beneficial when received post-surgery. Surgery that targets any soft tissue structure can result in an increase in scar tissue. Scar tissue is made up of type 3 collagen, which is laid down in a hazardous format which can affect the tissues ability to elongate and function. Massage can target scar tissue and break up the adhesive connections within the hazardous format, enabling the tissues to realign in a longitudinal and more functional fashion. The reduction in scar tissue achieved following a surgical procedure can reduce pain, improve range of movement and increase flexibility.
Massage can be beneficial to an individual suffering from tight muscles due to their neurological condition. Tightness within muscle are common in neurological disorders such as Parkinson's, cerebral palsy and epilepsy which can cause pain, reduced flexibility and overall function. Massage can target tight muscles through increasing the temperature within tissues, this is achieved through stimulating vasodilation, a winding of blood vessels and increased blood circulation. Massage can target adhesive fibre connections which are present within tight muscles by applying deep compressive forces. A reduction in muscular tightness can also reduce pain, improve flexibility and range of movement.
What are the physiological effects of a massage for neurological disorders?
The application of massage can produce a number of physiological changes to an individual with a neuromuscular disorder. The physiological effects of massage include;
Massage can increase cellular exchange. The application of massage can stimulate an increase in blood circulation through a process of vasodilation. Vasodilation refers to the widening of blood vessels as the smooth muscles surrounding the vessels relax. An increase in blood circulation can increase cellular exchange as blood carrying oxygen and nutrients are readily brought to the tissues and waste products and toxins are taken away. An increase in cellular exchange can result in a reduction of pain, the maintenance of healthy muscles and improved performance.
Massage can increase the release of endorphins, serotonin and dopamine. The application of massage can stimulate the autonomic nervous system which increases the release of natural endorphins. Endorphins are released during times of happiness and pleasure. Low levels of endorphins are linked to negative thoughts, anxiety and depression. An increase in the release of endorphins such as serotonin and dopamine can overall increase happiness and well-being. An increase in serotonin levels can promote feelings of happiness and relaxation. An increase in the levels of dopamine can promote feelings of enthusiasm and motivation.
Massage can increase tissue elasticity. Tissue elasticity refers to the tissues ability to elongate under stress. A high level of tissue elasticity can reduce the risk of injury, maximise performance and increase flexibility. Massage has the ability to increase tissue elasticity by stimulating an increase in blood circulation which increases the temperature of the tissue. An increase in tissue temperature allows the tissue to become more elastic, pliable and flexible.

What are the benefits of a massage for neurological disorders?
There are a number of benefits which can be achieved following the application of massage for an individual with a neurological disorder such as;
Massage can increase tissue flexibility. A reduction in tissue flexibility can be experienced by an individual with a neurological disorder due to a number of reasons such as an increase in type 3 collagen or alterations in muscular activity. Massage can increase tissue flexibility through prompting a number of physiological changes, which include a reduction in scar tissue and an increase in tissue temperature. Massage can reduce the presence of scar tissue by applying compressive forces which break up the adhesive fibre connections allowing the collagen fibres to realign. Massage can increase tissue temperature by prompting an increase in blood circulation through vasodilation. An increase in tissue temperature allows the tissue to relax and become more pliable and flexible.
Massage can decrease muscular tension. Massage treatment has the ability to reduce muscular tension through breaking down scar tissue, increasing tissue temperature and the removal of waste products. Deep massage strokes can break down scar tissue by breaking and separating adhesive connections between muscular fibres. Massage can increase tissue temperature by stimulating vasodilation which increases blood flow. Massage can increase the removal of waste products through stimulating capillarisation. Capillarisation refers to an increase in the number of capillaries within one area. Capillaries are vessels responsible for cellular exchange therefore an increase in the number of capillaries means an increase in cellular exchange.
Massage can increase range of movement. This is achieved through a number of physiological changes stimulated through the application of massage such as an increase in tissue temperature, a decrease in scar tissue and swelling. An increase in tissue temperature is achieved through the stimulation of vasodilation which increases blood circulation. A reduction in scar tissue is achieved through applying compressive forces which break up the adhesive type 3 collagen connections. A reduction in swelling is achieved through assisting with the lymphatic system to drain excessive lymphatic fluid towards the body's lymph nodes.
Massage can decrease pain. Pain can be reduced through the application of massage due to the pain gate theory and an increase in the release of endorphins. The pain gate theory states impulses sent from a harmful stimulus e.g. inflammation can be blocked by the impulse of a non-harmful stimulus e.g. massage. Massage has the ability to reduce the feeling of pain through blocking impulses sent from harmful stimuli traveling up the spinal pathway to the brain. Massage can stimulate the release of endorphins such as serotonin and dopamine through stimulating the autonomic nervous system. An increase in the levels of endorphins can leave the individual feeling a reduction in pain and an increase in relaxation and calmness.
Massage can reduce feelings of stress. During times of high stress or threat the hypothalamus stimulates an increase in the release of cortisol. Low levels of cortisol can be beneficial as it enables the individual to feel alert and observant. If levels of cortisol remain high for prolonged periods of time the individual can be left feeling anxious, depressed and stressed. Massage can reduce the production of cortisol by promoting relaxation.
Summary
Massage treatment can be beneficial to an individual managing a neurological disorder in both a physical and psychological sense. Massage can be extremely beneficial when applied during times of chronic pain, high muscle tone, post-surgery and tight muscles. Massage can produce a number of physiological effects such as increased cellular exchange, endorphins release and tissue elasticity. The massage treatment received can produce a number of benefits such as increased flexibility and range of movement and decreased tension, pain and stress.
How can I arrange a massage to help neurological disorders?
To arrange a massage to help neurological disorders at Physio.co.uk, email us at office@physio.co.uk or call us on 0161 883 0077.
You can also book an appointment online and save £10.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800