What is sensory integration?
Sensory integration is the process by which the brain interprets sensory information and forms an appropriate response. Sensory integration enables us to participate in everyday life with ease and perform many skills and actions automatically. Typically, children are able to do this automatically. However, some children are unable to understand and deal with the sensory information they receive, or react to it effectively. This affects their potential to interact with the environment surrounding them. This difficulty is known as sensory integration disorder.
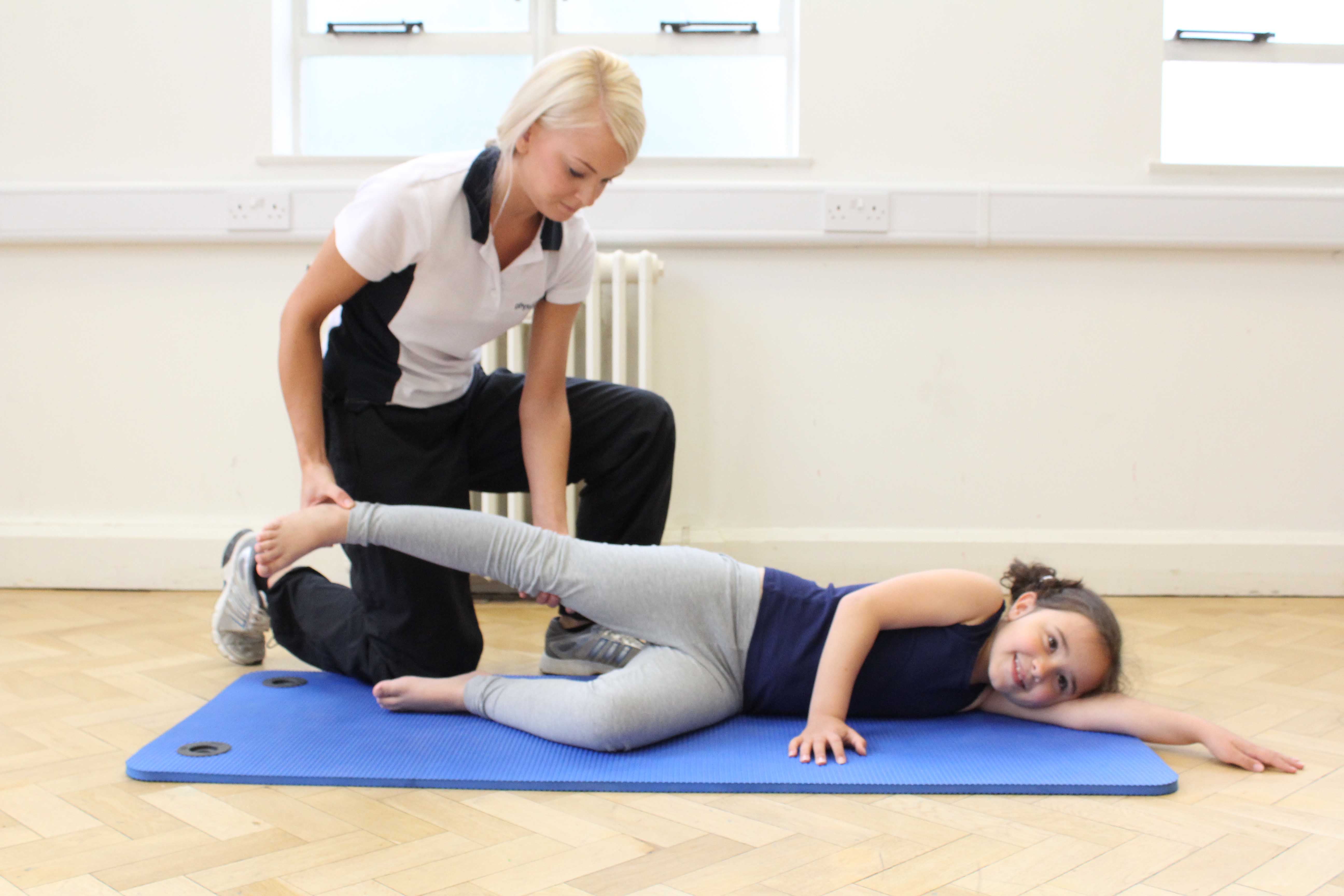 Above: Sensory exercises using a resistance band and gym ball
Above: Sensory exercises using a resistance band and gym ballWhat causes sensory integration disorder?
Neurological disruption leading to sensory integration disorder occurs in three ways:
- the brain not receiving sensory messages
- Sensory messages being received inconsistently
- Sensory messages being received consistently, but not connecting with other sensory messages effectively
- Autism and other developmental disorders
- Premature birth
- Stress-related conditions
- Learning disabilities
- Substance abuse due to learning disabilities
- Brain injury
- Fragile X syndrome
- Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
What are the symptoms of sensory integration disorder?
Symptoms of sensory integration disorder will vary, and children will experience them in different ways. It is difficult to distinguish symptoms from other conditions or problems. Symptoms of children with sensory integration disorder include:
- Distracted very easily / reduced attention span
- Unable to calm themselves down
- Enjoy strong rhythmic movements
- Difficulty with balance and poor saving reflexes
- Hypersensitive / hyposensitive to movement, sound, touch or sight
- Delayed academic achievement / specific learning difficulty
- Abnormally high / low activity level
- Emotional problems
- Social difficulties
- Problems organising their movements and actions
- Clumsiness or noticeable lack of care
- Lack of self-control
- reduced body awareness
- Delay in motor skills, speech, or language development
What can physiotherapy do to help sensory integration disorder?
Physiotherapy can also offer a sensory integration programme. School based and home activities are far more beneficial for some children, rather than utilising special rooms with equipment. Children might benefit more from using a sensory integration approach whereby the specialist physiotherapist or occupational therapist can offer guidance regarding activities which can be carried out in the comfort of school and home surroundings.
Some practical activities that can be used to promote the vestibular or proprioceptive senses include:
- rebound therapy
- massage
- swinging in a blanket/hammock/swing
- hydrotherapy
- increasing body awareness
- stretches
- rolling/ bouncing on a gym ball
- experiencing large movements and movement through space
- Crawling/climbing under and over large cushions, bean bags, apparatus, etc.
- hydrotherapy
Summary
Sensory integration is the process by which the brain interprets sensory information and forms an appropriate response. Some children however are unable to understand the information they receive or react to it effectively – this is known as sensory integration disorder. A number of factors can contribute to this disorder including autism, premature birth, brain injury and stress related conditions. Children affected with the disorder may display a number of symptoms including being very easily distracted, hypersensitive/hyposensitive to movement, touch, sound, or having an abnormally high/low activity level. Specialist physiotherapists can help children with sensory integration disorder.
To arrange an appointment with Physio.co.uk call now on 0330 088 7800 or for more information please contact us.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800