What is paediatric hypertonia?
Hypertoniain children is characterised by an abnormal increase in tension within the muscles of the body. Hypertonia causes the reduced ability for a muscle to stretch, which can lead to contractures. Resulting contractures can cause a decreased range of movement and loss of function.
Muscle tone is the resistance of muscles to stretch. Normal muscle tone is controlled by the central nervous system and is high enough to resist the effects of gravity but low enough to allow full freedom of movement.Correct muscle tone is essential for a person to be able to stand up, sit up and function properly. Physiotherapy uses a variety of treatment methods to help reduce hypertonia and improve function.
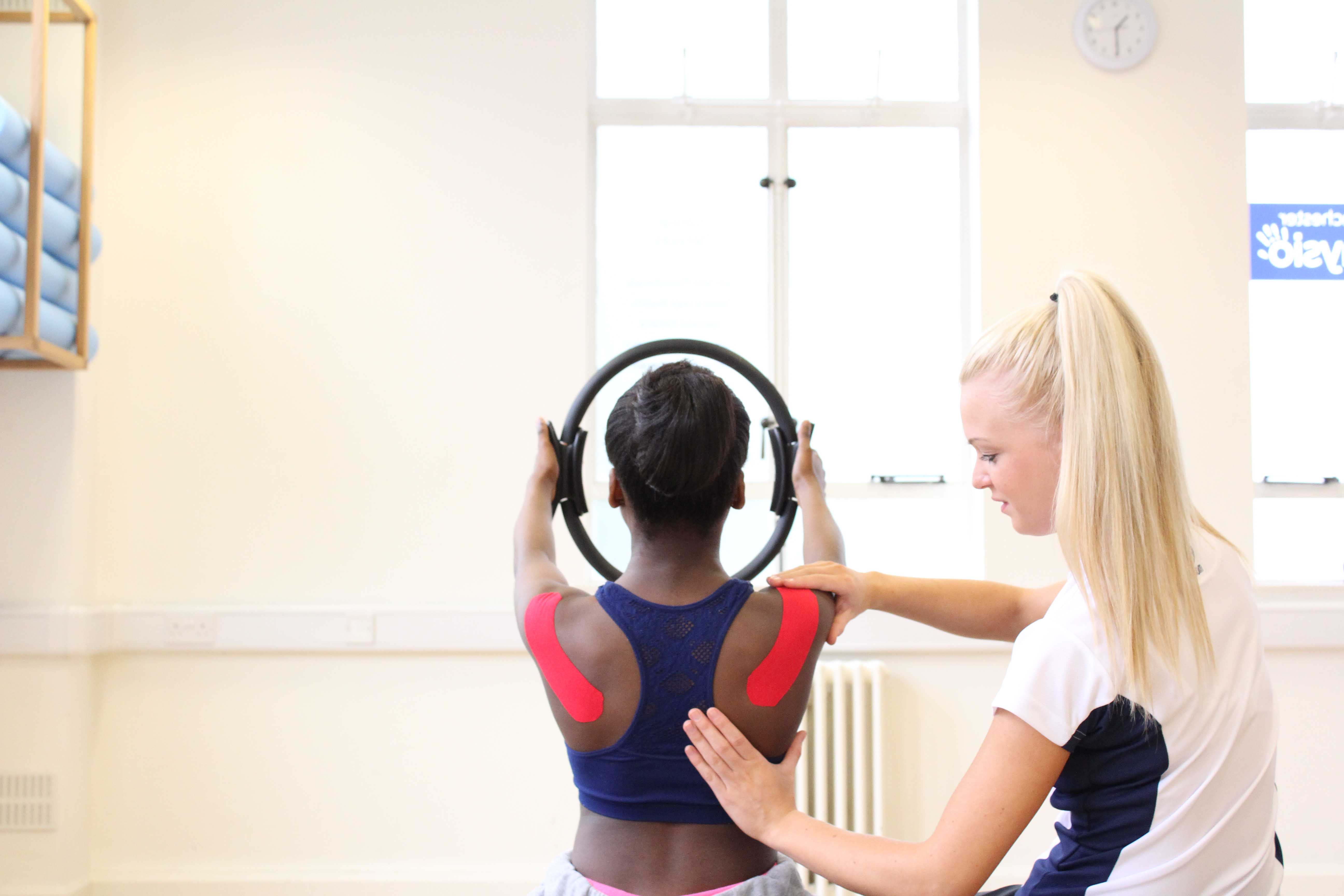 Above: Passive stretches to help lower tone
Above: Passive stretches to help lower toneWhat can cause hypertonia in children?
Hypertonia can be caused by disruption to the nerve pathways in the central nervous system that are responsible for switching on or off muscle activity. These nerve pathways carry information from the central nervous system to the body to control muscle tone and posture. Injury or damage to these nerve pathways of the central nervous system results in the interruption of messages from the brain to the body causing abnormalities in muscle tone. Hypertonia is often seen in children or adults with cerebral palsy, stroke or after a severe head or spinal cord injury. The condition can also be related to spasticity and dystonia.
 Above: Cervical spine / neck massage to lower tone
Above: Cervical spine / neck massage to lower toneWhat are the symptoms of hypertonia in children?
The symptoms associated with hypertonia include;
- Loss of function
- Decreased range of movement
- Rigidity of muscles
- Spasticity of muscles
- Deformity
- Tenderness and pain in the affected muscles
- Rapid muscle contractions
- Involuntary crossing of legs
- Fixed joints
What can physiotherapy do to help children with hypertonia?
A number of treatments can be used to treat hypertonia, including:
Postural management
As a large number of muscles will be contracted and tightened, the child’s posture is likely to be affected. Treatment is focused on relaxing the child and trying to make the body less tense so that their posture is more of a natural position.
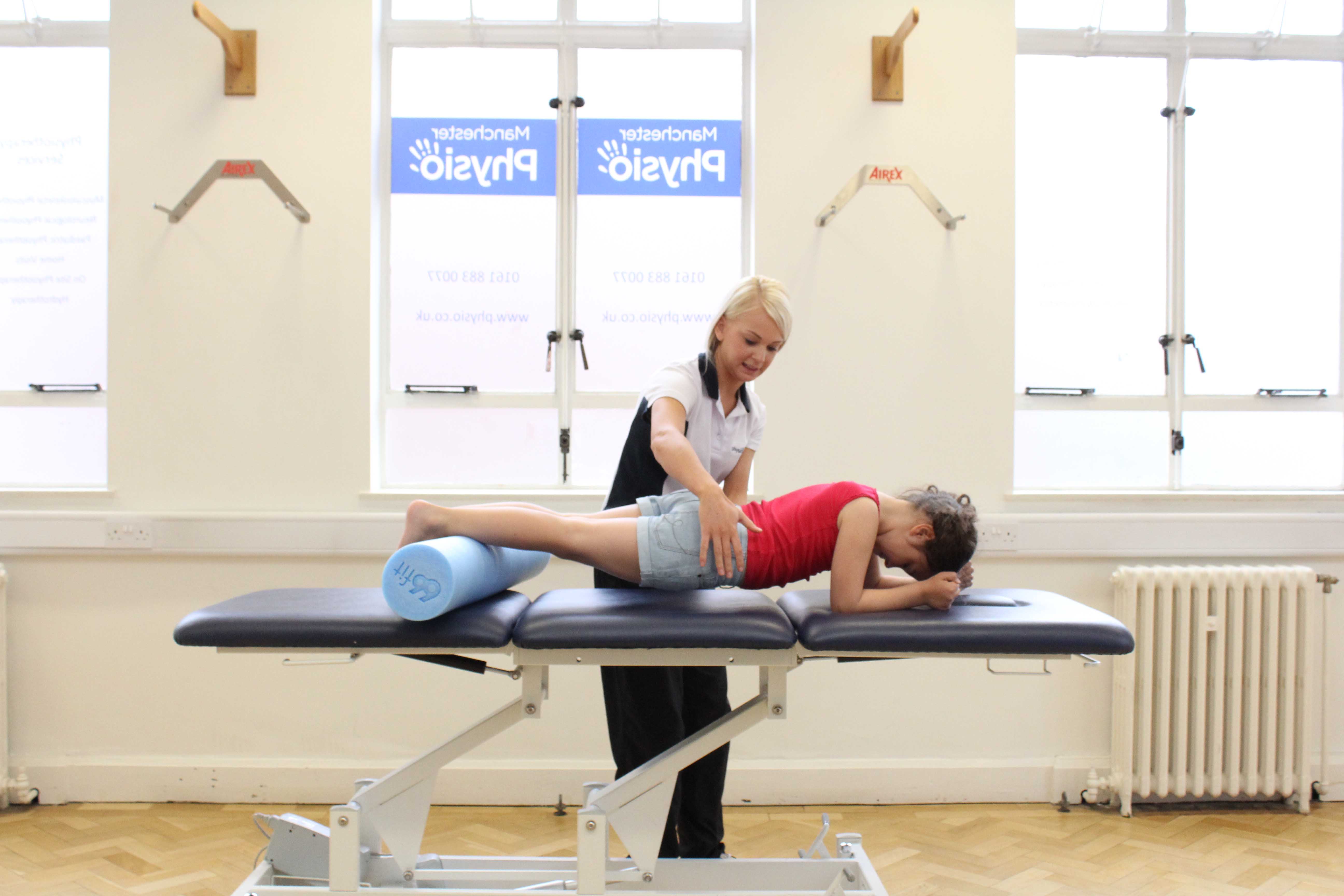
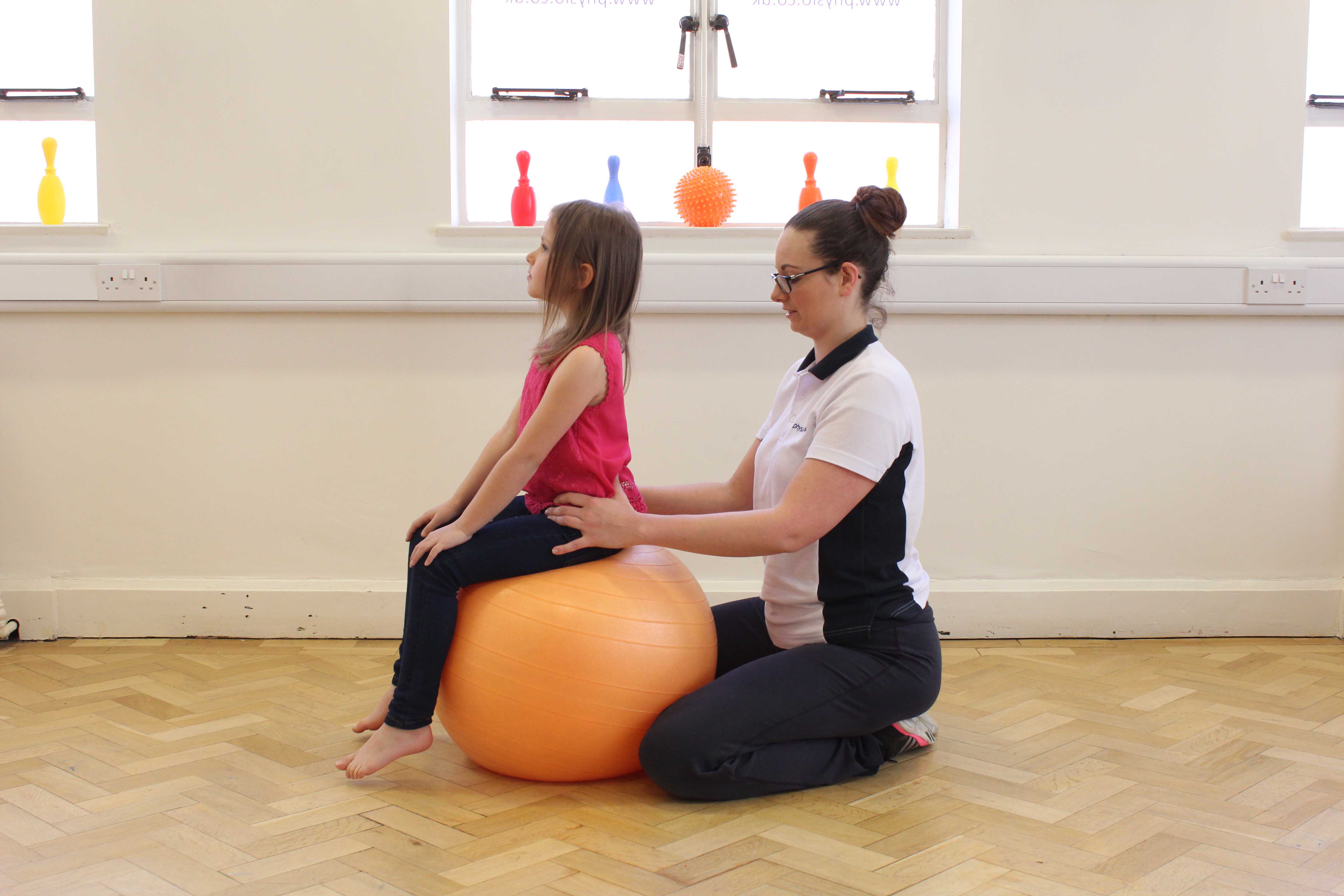 Above: Passive stretches of the legs to lower tone
Above: Passive stretches of the legs to lower toneStretching programme
Due to the muscle contractions, the child’s limbs may be out of position and they may not be able to move them freely. Stretching of the muscles can help to lengthen the contracted muscles and as a result the child may be able to move their limb’s more freely.
Orthotics
These can be used alongside a stretching programme to position a limb so that the right muscles are being stretched even when the child is relaxed. This can help to lengthen affected muscles.
Facilitating normal movement
The child’s movement patterns may be affected due to tension and contractures. Along with the other treatment, everyday activities can be practiced by working on the movements needed to achieve these activities.
Summary
Hypertonia is a condition that is characterised by abnormal increase in a child’s muscle tone. Normal muscle tones allow the body to freely move whilst resisting against the effects of gravity. Muscle tone helps posture and allows a person to stand up, sit up and function effectively. Hypertonia can be caused by injury to the central nervous system or spinal cord causing disturbances in the nerve pathways that are responsible for muscle tone. Symptoms of hypertonia include loss of function, decreased range of movement, deformity and muscle stiffness. Physiotherapy is a highly effective method of treatment to help decrease the effects of hypertonia. Specialist physiotherapists at Physio.co.uk can provide your child with a thorough assessment and treatment programme which may include activities such as muscle stretching and techniques to help facilitate normal movement.
To book an appointment or for more information about paediatric hypertonia contact us or call 0330 088 7800.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800