What is trochanteric bursitis?
A bursa is a fluid-filled sac which allows the tissues of the body to slide over one another without friction. The tronchanteric bursa is located on the point of the hip (the greater trochanter). Trochanteric bursitis is inflammation and swelling of this bursa. Physiotherapy can successfully treat trochanteric bursitis.
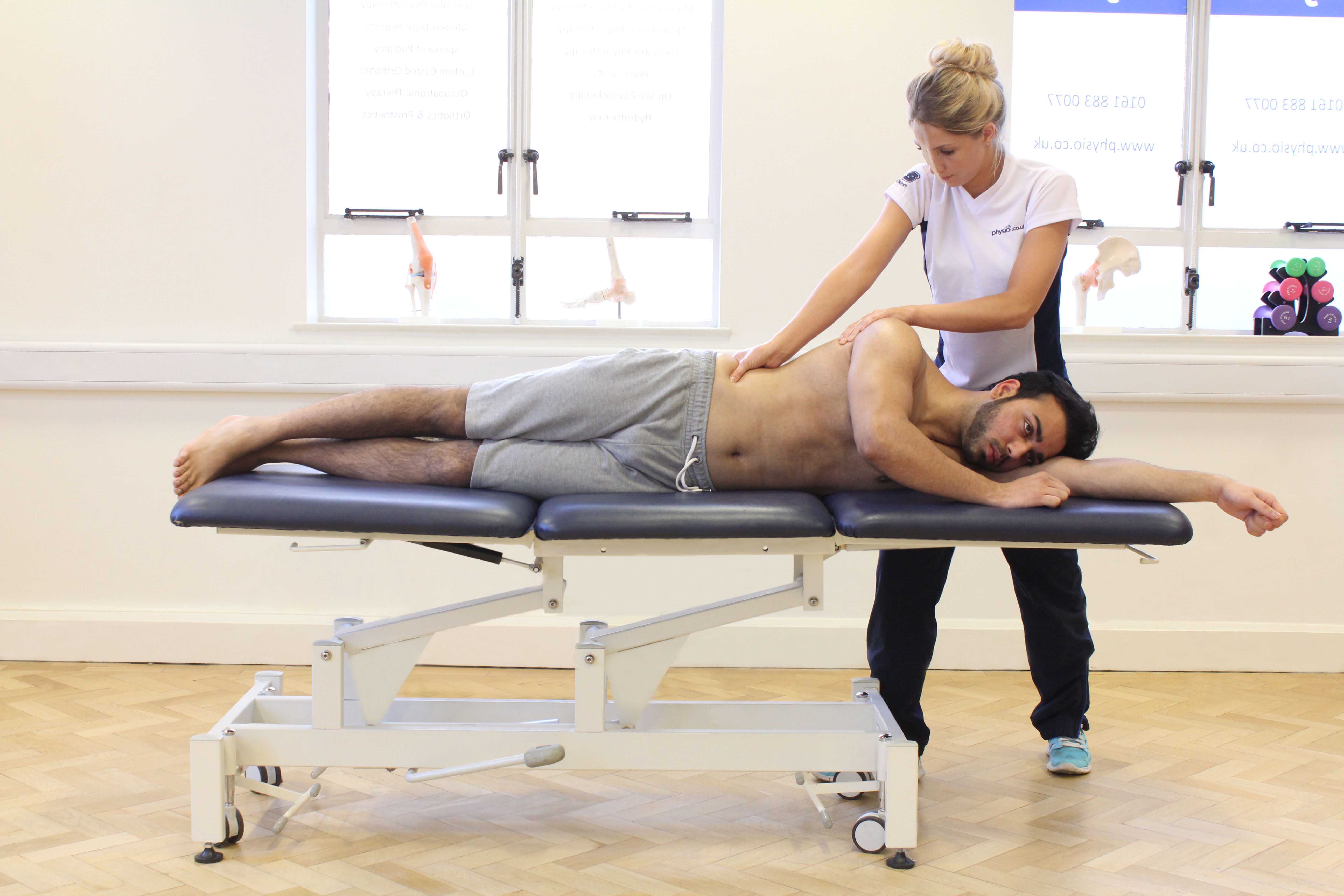
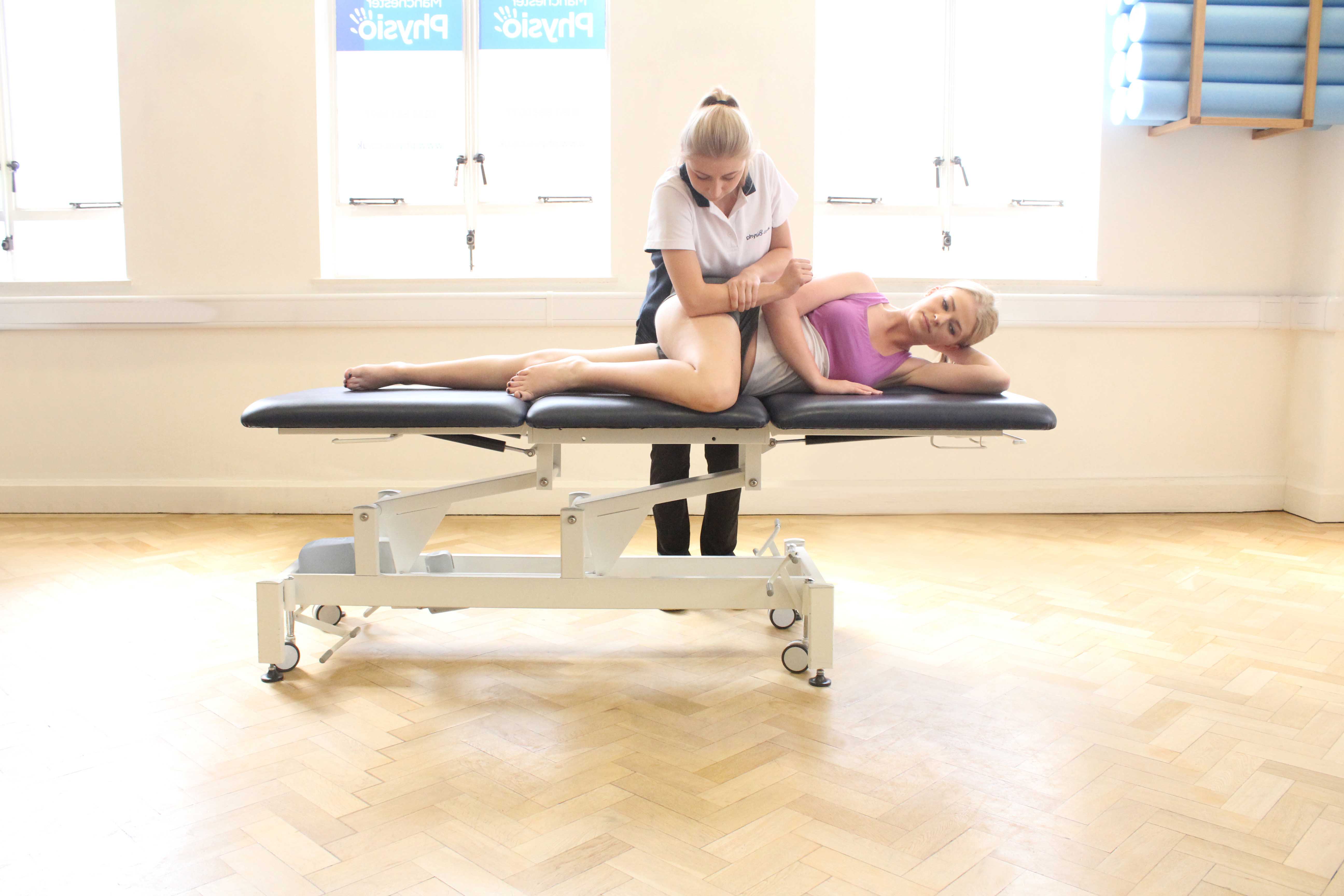 Above: Deep tissue massage of the muscle and connective tissues around the hip.
Above: Deep tissue massage of the muscle and connective tissues around the hip.How does trochanteric bursitis happen?
Bursitis is normally caused by the irritation of a bursa. The trochanteric bursa works to allow the gluteal muscles (muscles at the back and side of the hip) to slide smoothly over the point of the hip. Excessive tightness in these muscles can increase the pressure and friction on the bursa. This increases wear and tear to the bursa and, over time, can cause in thickening of the bursa, inflammation and bursitis.
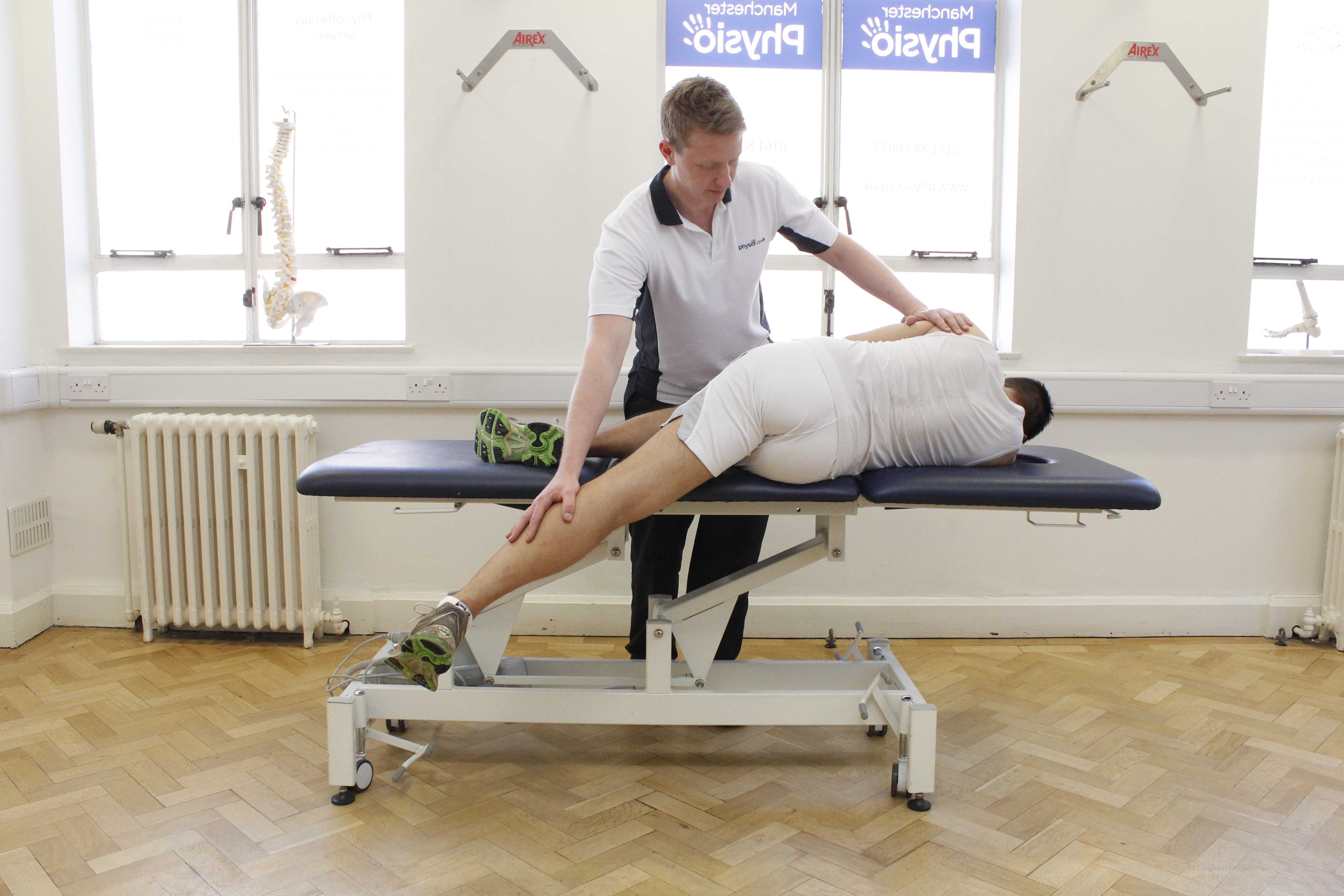
 Above: Passive stretch of the muscles and connective tissues of the hip by specialist therapist
Above: Passive stretch of the muscles and connective tissues of the hip by specialist therapistWhat are the symptoms of trochanteric bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis causes pain at the point of the hip. The pain is normally confined to one specific place near the point of the hip and is very tender to touch. In some cases the pain also radiates along the outside of the upper leg to the knee. The pain is often aggravated by activities such as walking, running, climbing the stairs, crossing your legs and getting in and out of the car. Other symptoms may include:
What should I do if I have trochanteric bursitis?
If you have trochanteric bursitis you should avoid activities that aggravate your pain and arrange an assessment with a physiotherapist as soon as possible. Although the pain is often relieved with rest, the pain will only return as you try to return to normal activity if the cause is not addressed.
 Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapist
Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapistPhysiotherapy treatment for trochanteric bursitis.
Physiotherapy is very important in the treatment of trochanteric bursitis. Your physiotherapist will be able to provide you with a diagnosis and utilise a number of treatment techniques to minimise your pain. Treatment varies dependent on the cause of your condition but often involves:
What shouldn’t I do if I have trochanteric bursitis?
If possible, you should not continue with activities that make your pain worse. This is because these activities will irritate the bursa further, and possibly delay recovery.
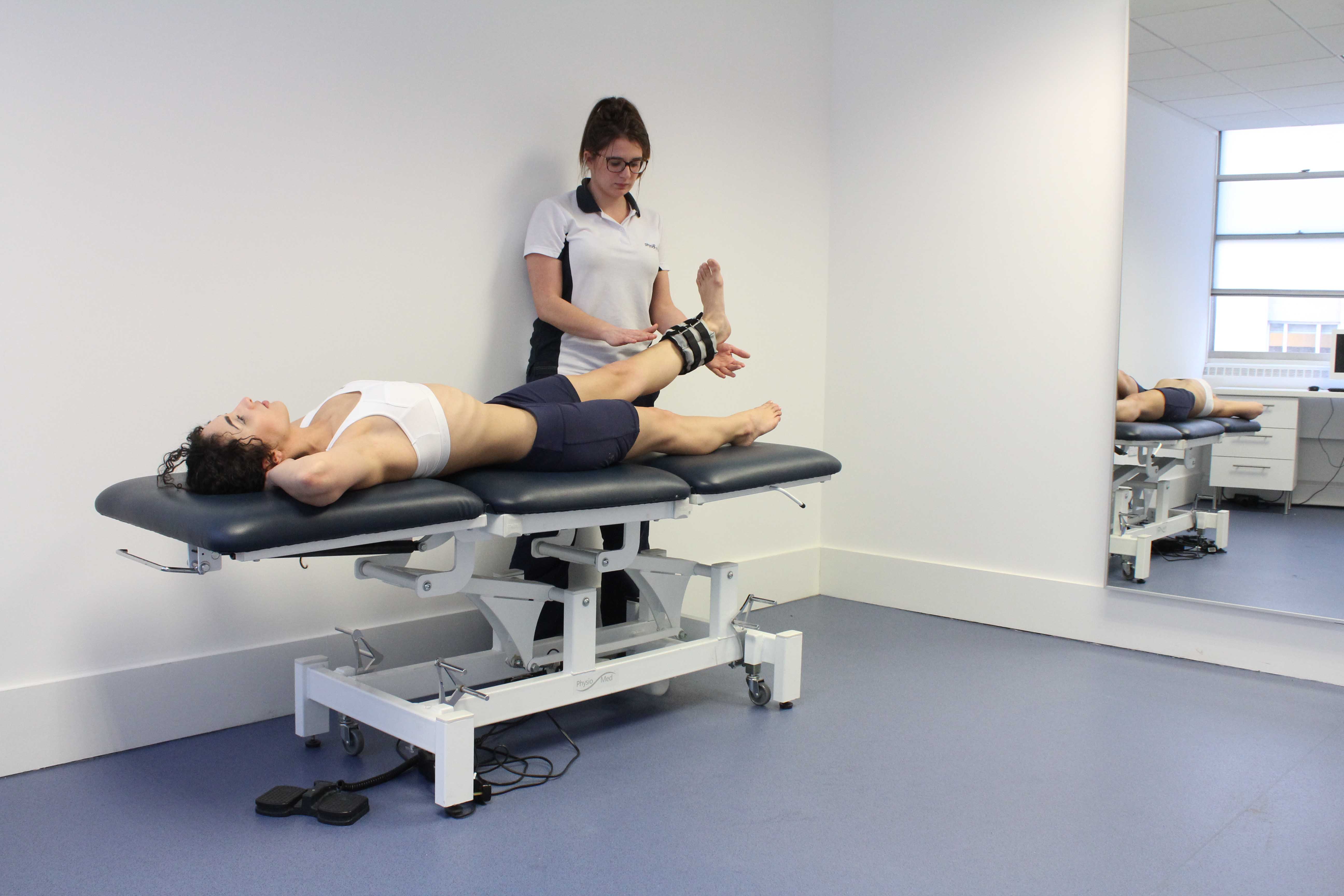 Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapist
Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapistCould there be any long-term effects from trochanteric bursitis?
If not treated correctly (or sometimes even with the correct treatment), trochanteric bursitis can sometimes develop into a chronic condition. In these situations the referral for the injection of a small amount of anti-inflammatory directly into the bursa may be required to reduce inflammation and stimulate healing.
To arrange a physiotherapy assessment call Physio.co.uk on 0330 088 7800 or book online.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800