What are deep breathing exercises?
Deep breathing exercises, often referred to as thoracic expansion exercises aim at getting the biggest breath of air possible into the lungs to help move any secretions (phlegm) that may be present at the bottom of the lungs, and increase lung volumes.
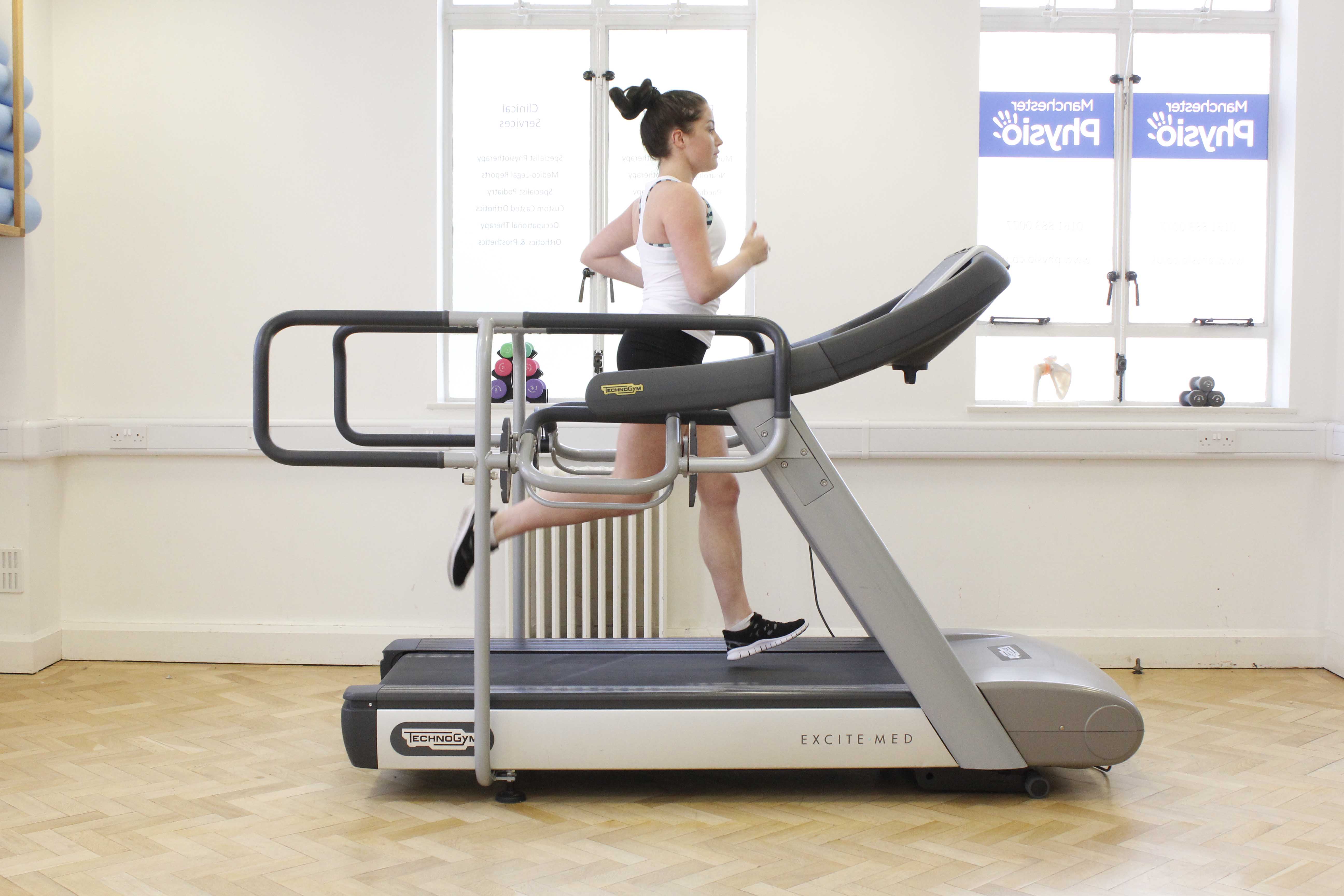 Above: Improving lung function and exercise tolerance through exercise supervised by a specilaist physiotherapist
Above: Improving lung function and exercise tolerance through exercise supervised by a specilaist physiotherapistDeep breathing exercises form a stage of the active cycle of breathing exercise, and tend to be carried out in a sitting position. It is advised you place your hands on your lower rib cage so you can feel the air entering the bases of your lungs, keeping your shoulders still, you are aiming for as much movement of your ribs upwards and outwards as possible.
What are the benefits of deep breathing exercises?
The main benefit of deep breathing exercises is to allow air to get right to the bottom of the lungs to help mobilise secretions, by clearing secretions you significantly decrease the risk of developing a chest infection. Other benefits include:
- Improved respiratory function (gas exchange)
- Increased lung volumes
- Improved chest expansion
- Promote relaxation
- Reduce reliance on oxygen therapy (if applicable)
- Can be combined with manual techniques such as percussion, vibration, or practised in postural drainage positions
- Can be carried out independently by patient with no need for supervision
- Can be carried out in a number of positions, from sitting watching television, to lying in bed.
Who would benefit from deep breathing exercises?
Deep breathing exercises are beneficial in all respiratory patients, not only to mobilise secretions but to generally enhance lung function and prevent atelectasis (areas in the lungs where gas exchange is unable to occur). Respiratory conditions that are likely to benefit from thoracic expansion exercises include:
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
- Following surgery
- Pneumonia
- Obstructive respiratory conditions – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), emphysema, severe asthma, chronic bronchitis
- Bronchiectasis

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800