What are Pranayama breathing techniques?
Pranayama breathing is a controlled breathing technique used in yoga; it focuses on correcting your breathing technique so oxygen is delivered to the blood and brain effectively.
The technique consists of a cycle that emphasises pauses in breathing without forgetting the importance of full exhalation. There are four stages in the cycle:
- Puraka (Inhalation) – Smooth and continuous process of drawing in air.
- Abhyantara Kumbhaka (Pause after inhaling) – Sometimes referred to as a full pause, this is the deliberate holding of air in the lungs following a full inhalation, without any movement of lungs, muscles or any part of the body.
- Rechaka (Exhalation) - smooth and continuous breathing out through relaxation of the tensed muscles. Such relaxation forces air from the lungs as they return to a relaxed state.
- Bahya Kumbhaka (Pause after Exhaling) Sometimes referred to as an empty pause, this is the deliberate holding of breath prior to taking the next breath in.
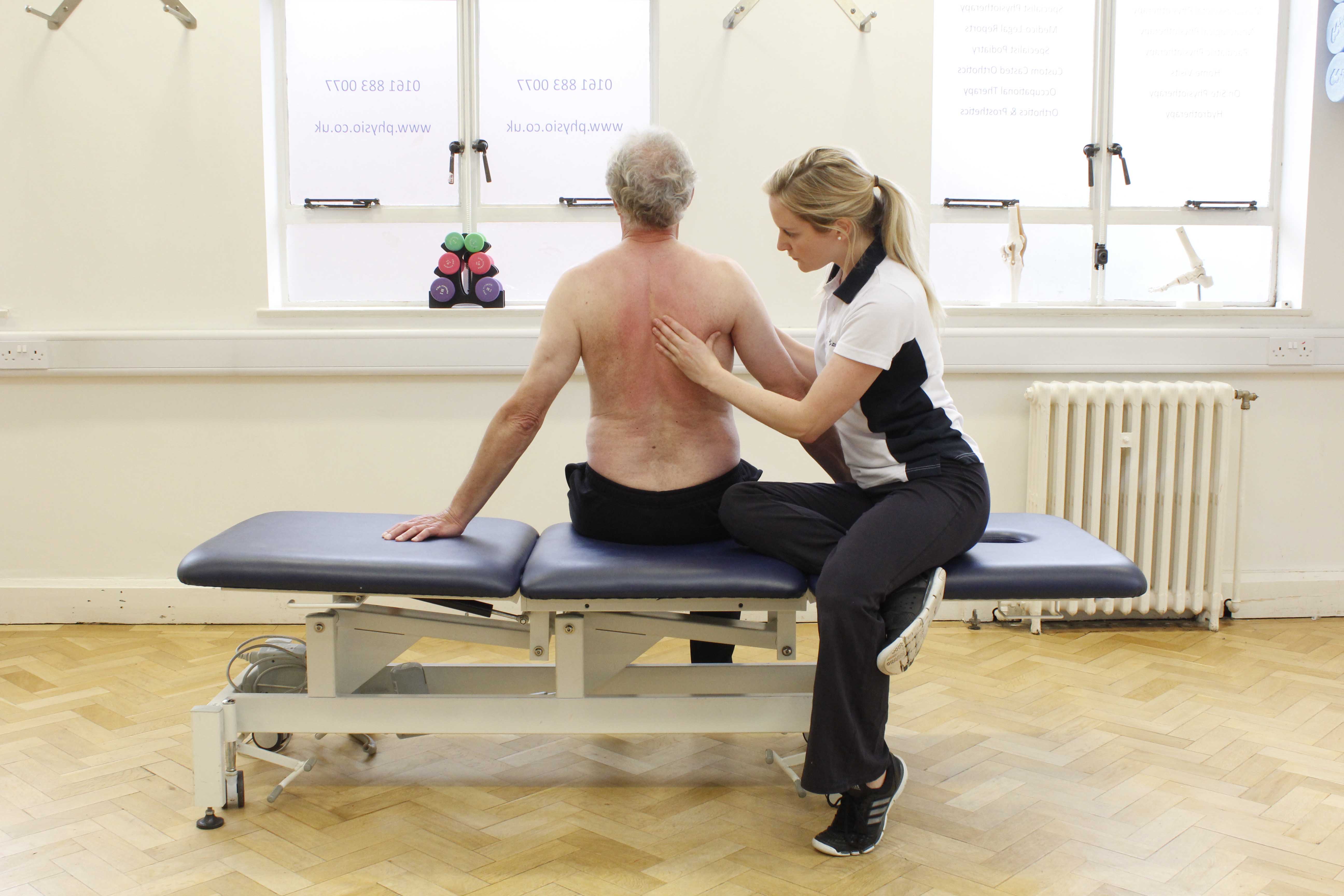 Above: Active cycle of breathing exercises supervised by a specialist physiotherapist
Above: Active cycle of breathing exercises supervised by a specialist physiotherapistWhat are the benefits of Pranayama breathing techniques?
The Pranayama breathing technique teaches us to breathe properly, this means slowly and deeply. When carried out correctly, the technique has a number of benefits including:
- Increased lung volumes
- Improved lung function
- Relaxation
Who would benefit from Pranayama breathing techniques?
Pranayama breathing technique is beneficial for any person with a respiratory condition that causes them to experience dyspnoea (shortness of breath). Respiratory conditions include:
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Emphysema
- Chronic bronchitis
- Hyperventilation syndrome

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800