What is a superior tibiofibular joint injury?
The superior tibiofibular joint is the joint between the shin bone (tibia) and the smaller bone (fibula) that runs alongside it. The superior tibiofibular joint is located on the outside surface of the leg, just below the knee joint. A superior tibiofibular joint injury occurs when the joint or its supporting structures are damaged. Physiotherapy is important in the rehabilitation of a superior tibiofibular joint injury.
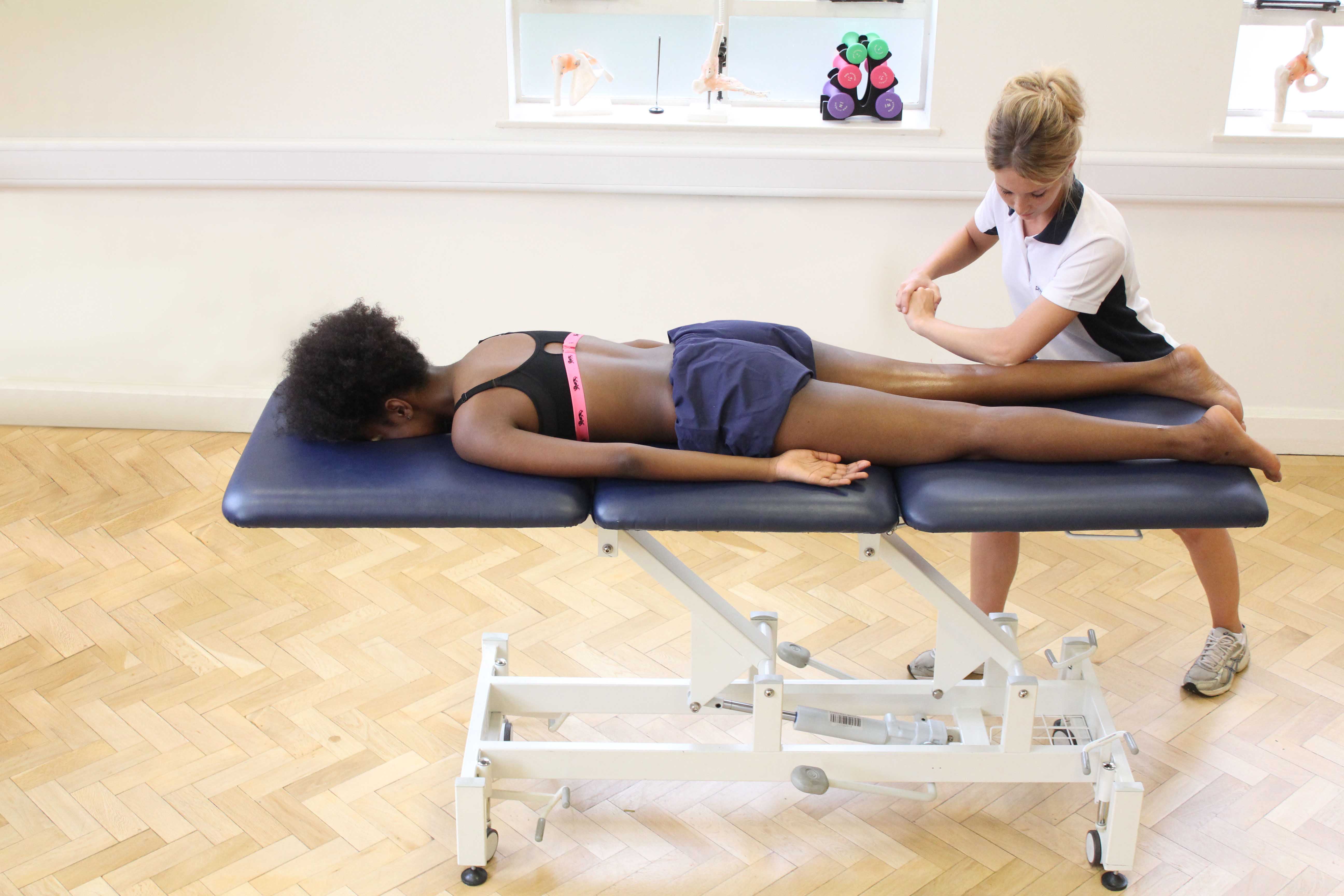 Above: Therapist performing soft tissue massage on the tissues aound the knee
Above: Therapist performing soft tissue massage on the tissues aound the kneeHow does a superior tibiofibular joint injury happen?
An injury to the superior tibiofibular joint can be caused by direct trauma to the joint or if the leg is twisted. A twisting injury often occurs when pivoting or suddenly changing direction whilst running and often occurs with a knee or ankle injury.
What are the symptoms of a superior tibiofibular joint injury?
Pain is felt on the outside of the leg, just below the knee if the superior tibiofibular joint is injured. Pain is usually worsened by activities that require rotation of the lower leg, such as pivoting or changing direction whilst running. Other symptoms may include:
What should I do if I have a superior tibiofibular joint injury?
The most important time in the initial treatment of a superior tibiofibular joint injury is the first 24–48 hours. This is because the majority of the bleeding and swelling around the injured joint occurs within this time. To control the amount of swelling and, therefore, accelerate your recovery, the injured leg should be rested and iced. Rest involves limiting the use of the injured leg, sometimes with the use of crutches. Ice should be applied to the injured site for 15–20 minutes every 1–2 hours. Ideally, using crushed ice or a bad of frozen peas wrapped in a moist cloth. Whilst completing this you should ensure that you contact your physiotherapist.
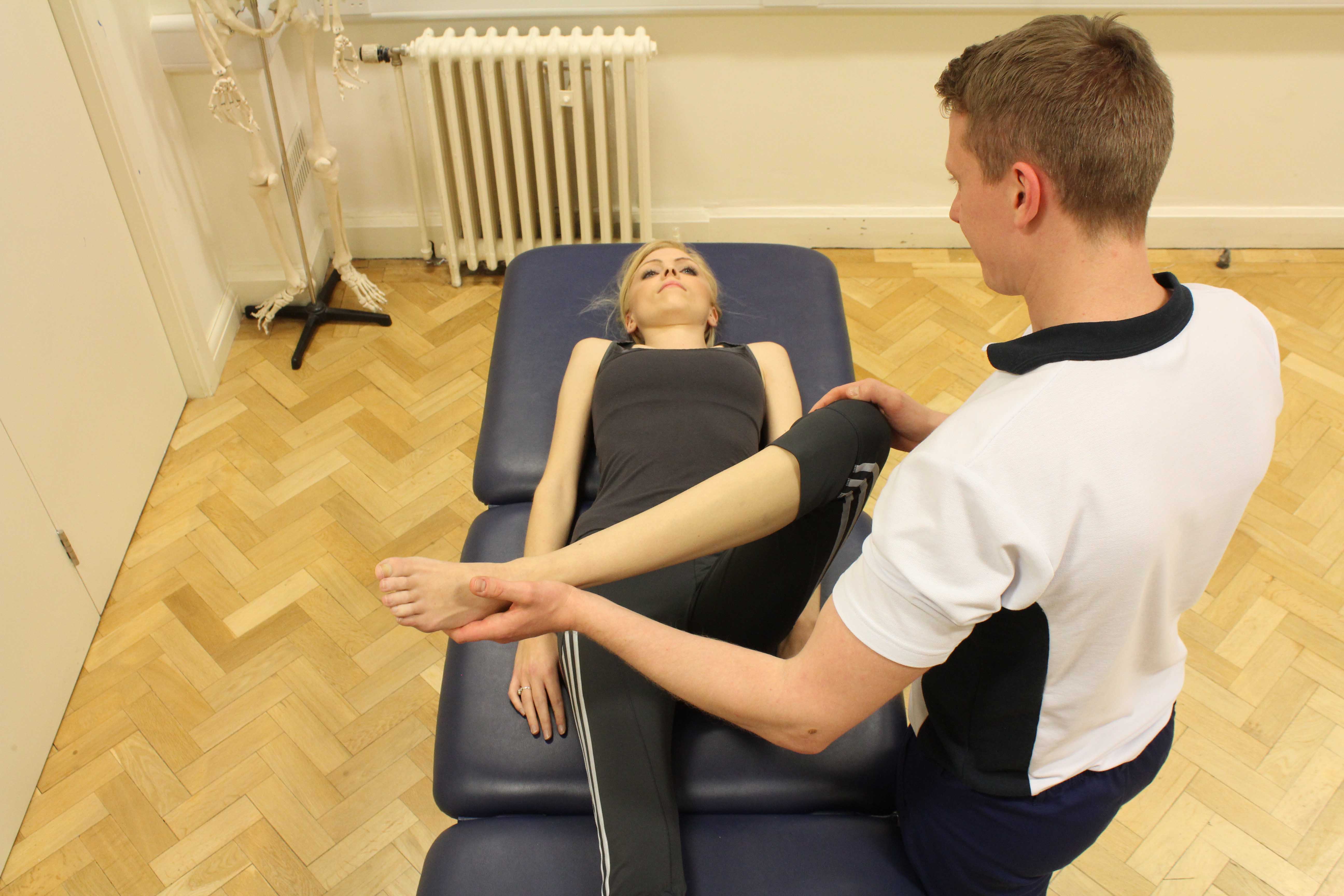 Above: Therapist performing knee assessment
Above: Therapist performing knee assessmentWhat shouldn’t I do if I have a superior tibiofibular joint injury?
Following an injury to the superior tibiofibular joint, you should avoid activities which increase blood flow to the injured area. These include hot showers, heat rubs, the consumption of alcohol and excessive activity. An increase in blood flow may increase the bleeding and swelling within the injured structures and potentially prolong your recovery.
Could there be any long-term effects from a superior tibiofibular joint injury?
If properly diagnosed and treated, an injury to the superior tibiofibular joint usually gets better within a few weeks and does not cause any long-term effects. If left untreated, there is a chance that it could lead to ongoing pain just below the outside of the knee.
Physiotherapy treatment for a superior tibiofibular joint injury.
Physiotherapy is important in the treatment of superior tibiofibular joint injuries. At your initial assessment, your physiotherapist can diagnose your problem and determine an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment for a superior tibiofibular joint injury may involve: To arrange a physiotherapy appointment call Physio.co.uk on 0330 088 7800 or book online.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800