What is it olecranon bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis (also known as ‘student’s elbow’), is the inflammation and swelling of a bursa in the elbow. The bursa is a fluid-filled sac that lies between the point of the elbow and the skin. Physiotherapy can effectively treat olecranon bursitis.
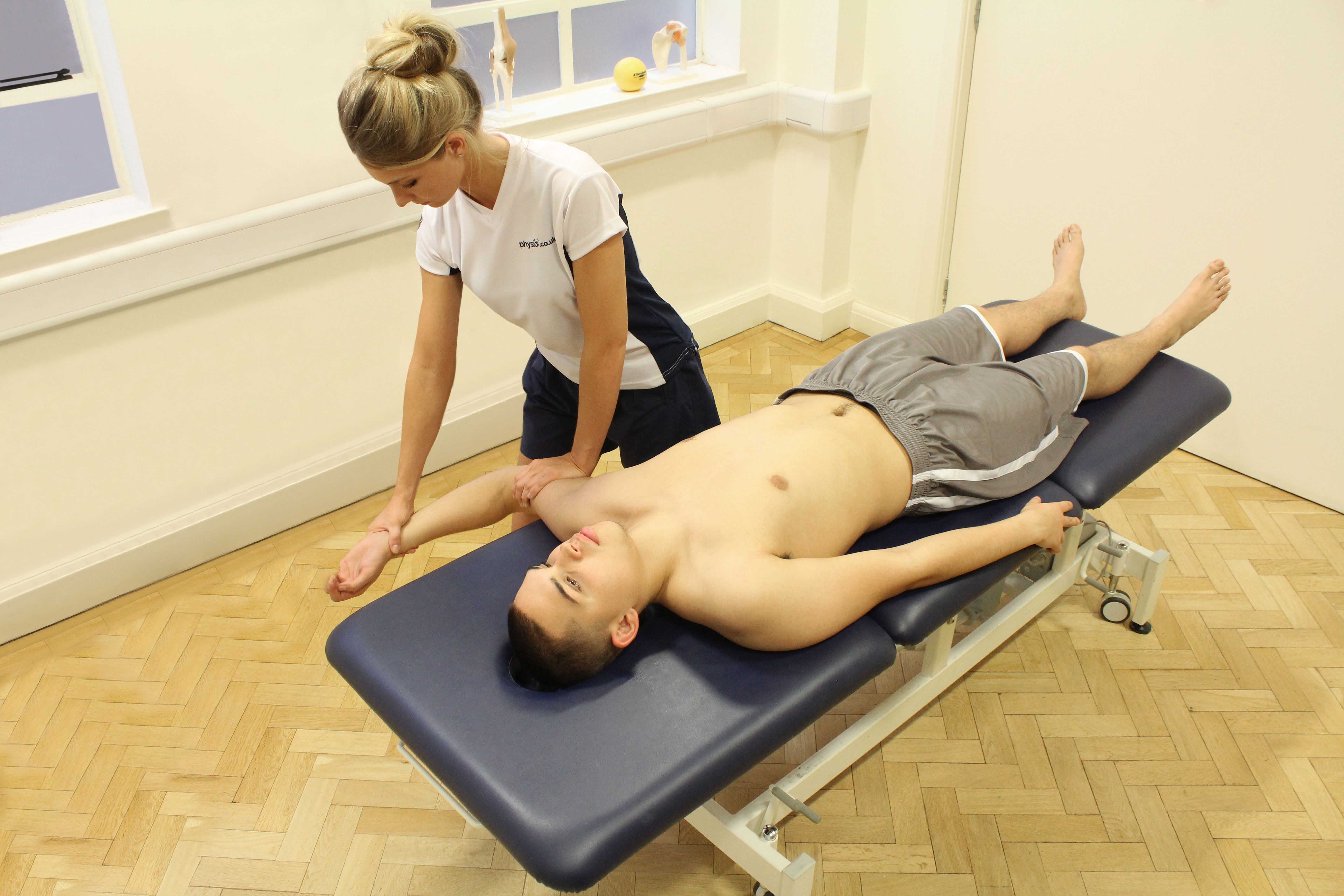 Above: Passive stretch of the elbow joint applied by the therapist
Above: Passive stretch of the elbow joint applied by the therapistWhat causes olecranon bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis occurs when the olecranon bursa is damaged or irritated. This can be caused by a direct blow to the point of the elbow. This can damage blood vessels within the bursa, causing bleeding. The blood in the bursa causes an inflammatory response, swelling of the bursa and, therefore, bursitis. Olecranon bursitis can also be caused by repeated minor trauma such as resting on your elbows on a hard surface for long periods of time such as when working or studying. This increases wear and tear on the bursa and, over time, can result in thickening of the bursa, inflammation and bursitis.
What are the symptoms of olecranon bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis causes pain and swelling over the point of the elbow. You may feel the pain most when you lean on your elbows or when you bend and straighten your elbow. The swelling may be sizable causing a large ‘egg shaped’ protrusion over the point of the elbow. Sometimes small lumps can be felt underneath the skin over the point of the elbow. These lumps are thickened areas of the bursal sac and can cause pain and the feeling that something is floating around under the skin. Other symptoms of olecranon bursitis include:
What should I do if I have olecranon bursitis?
The most important time in the treatment of any injury is the first 24–48 hours. Swelling is a necessary step in the healing process, but too much swelling can delay healing and cause further tissue damage. To limit the degree of damage to the elbow, the RICE regime should be commenced (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation). This will help to reduce blood flow to the injured area, thereby reducing the amount of swelling, pain and tissue damage.
You should avoid the activities you think may have caused your bursitis, such as leaning on your elbows on a hard surface. If this is not possible, you should take regular breaks and cushion the point of your elbow to reduce pressure on the bursa. Following this, you should consult your physiotherapist and sometimes your GP, as bursitis of this type can require active treatment in the form of anti-inflammatory drugs or an injection to resolve it.
Physiotherapy treatment for olecranon bursitis.
The assistance of your physiotherapist, and sometimes your GP, is important in the treatment of olecranon bursitis. In bursitis caused by an injury, they will able to assist in determining the extent of damage to the bursa and whether any of the surrounding tissues have been injured. From this, an estimation of how long your injury is expected to take to heal can be provided. Your physiotherapist can also use a number of treatment techniques to assist in reducing the pain and swelling, and enhance the healing of the injured structures. This will promote your return to activity.
In olecranon bursitis caused by repeated minor trauma, your physiotherapist will be able to assist in identifying the cause and how best to stimulate healing, thereby reducing your pain and swelling. In some situations, this may involve referral to your GP for draining of the swelling in the bursa, prescribing anti-inflammatory medications or injecting a small quantity of anti-inflammatory directly into the bursa to stimulate healing.
Other physiotherapy treatments include:
What shouldn’t I do if I have olecranon bursitis?
In the first few days following an injury to the olecranon bursa, you shouldn’t undertake activities which increase blood flow to the elbow. These include hot showers, heat rubs, massage, the consumption of alcohol and excessive activity. These can prolong bleeding in the bursa resulting in further swelling and an extended recovery. You also shouldn’t undertake any activity which involves resting on your elbows. This could further irritate the olecranon bursa, making the pain and swelling worse.
To arrange a physiotherapy appointment call Physio.co.uk on 0330 088 7800 or book online.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800