Types of lung disease
There are many different diseases that affect the respiratory system.
Inflammatory lung diseases cause inflammation of the small air sacs in the lungs called alveoli. This restricts the air flow in and out of the lungs and means the heart has to work harder to get oxygen from the lungs. Individuals with conditions such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) become short of breath and find it difficult to breathe during exercise.
Restrictive lung diseases such as infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS) restrict expansion of the lungs to their full capacity and cause shortness of breath.
Infections that affect the upper respiratory tractinclude the common cold, sinusitis tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis. Upper tract infections affect the nose, sinuses and pharynx or larynx.Lower respiratory tract infections affect the part of the respiratory system below the vocal cords and include pneumonia and tuberculosis.
Tumours affect the respiratory system such as small cell cancer, large cell cancer, lymphoma.Pulmonary vascular diseases affect the blood circulation in the lungs and include pulmonary embolism, pulmonary oedema and pulmonary haemorrhage.
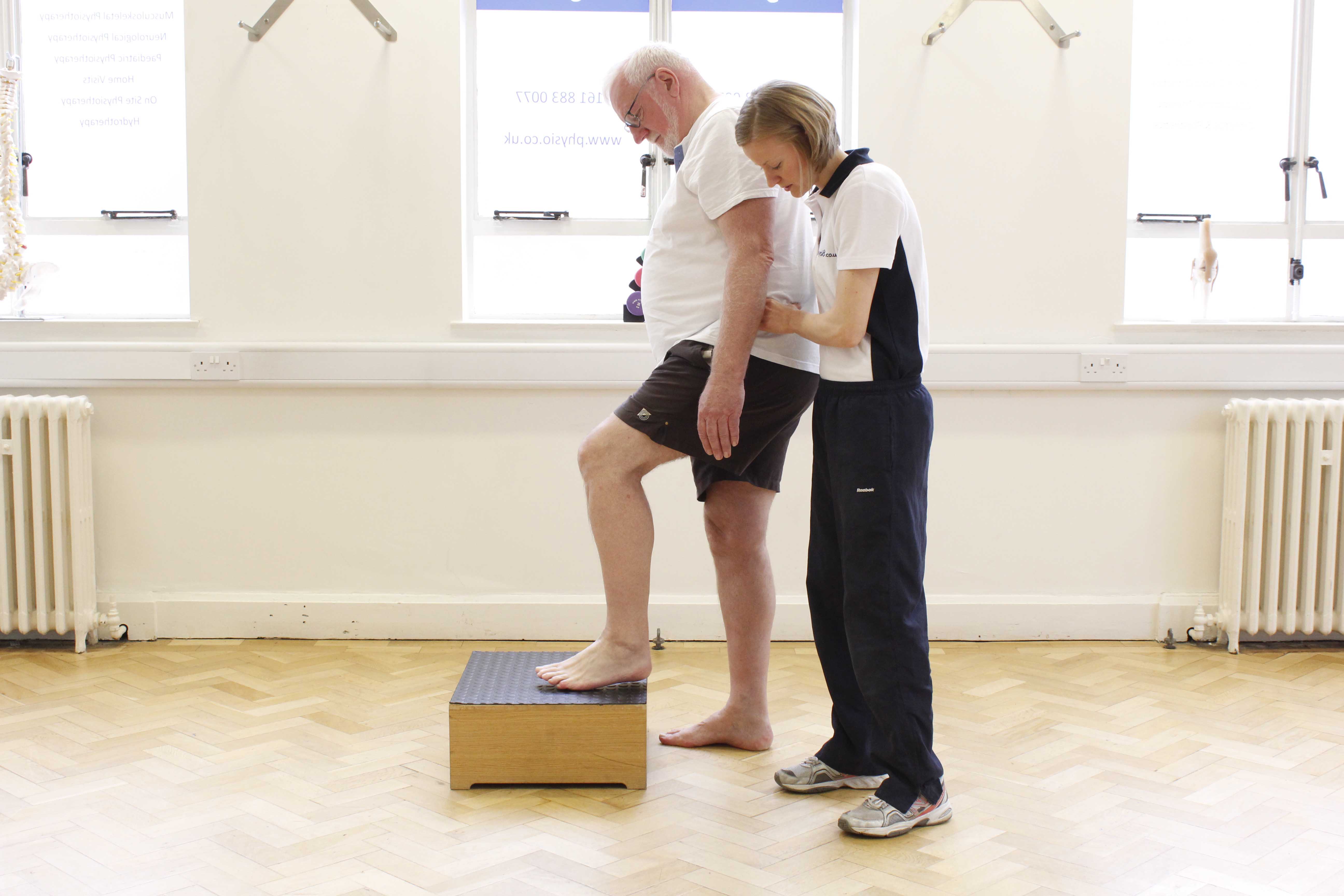 Above: Gentle cardio-respiratory tollerance exercises supervised by specialist MSK Physiotherapist
Above: Gentle cardio-respiratory tollerance exercises supervised by specialist MSK PhysiotherapistWhat are the symptoms of lung disease?
The symptoms of lung disease include breathlessness, a cough, a wheeze, production of phlegm and fatigue. If unmanaged, these symptoms can significantly limit exercise tolerance and mobility. Individuals with lung disease may become breathless whilst exercising, walking to the shops or using the stairs.
Diagnosis of lung disease
Respiratory diseases may be investigated using an X-ray, a computed tomography (CT) or ultrasound scan. A bronchoscopy allows a doctor to see inside the airways by inserting a camera called a bronchoscope through the nose or mouth. Depending on the suspected diagnosis it may be necessary to take a sample of lung tissue or phlegm for further analysis.
Treatment of lung disease
The treatment of lung disease depends upon the specific disease causing the symptoms and will be decided by a respiratory medicine specialist. General treatment for a respiratory condition includes smoking cessation advice, inhalers or medication to increase size of airway, provision of oxygen in the home and pulmonary rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy for lung disease
Specialist physiotherapy can provide substantial relief from the symptoms of lung disease. Following detailed assessment of your problems and symptoms, physiotherapy treatment of a respiratory condition is likely to involve:
- Patient education
- Symptom management
- Deep breathing exercises
- Active cycle of breathing
- Postural drainage
- Manual airway clearance techniques
- Gentle cardiovascular fitness training
- Pain relief
Individuals with lung disease significantly benefit from physiotherapy treatment. The benefits of regular physiotherapy sessions include:
- Maintain clear airways
- Reduce breathlessness
- Improve exercise tolerance
- Learn sputum clearance techniques
- Learn how to optimise positioning to maintain clear airways
- Learning breathing control exercises to do at home
- Take part in cardiovascular exercise under experienced supervision
- Decrease pain and anxiety
Why Physio.co.uk
At Physio.co.uk, we understand it is frustrating when your normal daily routine is limited by coughing and breathlessness. Our specialist physiotherapists have a clear understanding of the symptom management of lung disease and can teach you how to minimise your symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
- Caring, experienced physiotherapists
- No waiting lists
- Treatment at home or in the clinic
- Treatment at any stage of your condition
- Provision of a home exercise program
- Flexible appointment times
- Access to gymnasium

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800