- Damage to the sensory nerves can cause loss of sensation including numbness, tingling and pain
- Damage to the motor nerves can cause loss of motor function including weakness and difficulty walking.
- Damage to autonomic nerves can cause urine incontinence, constipation, diarrhoea, dizziness, fainting and impotence.
Diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy
A diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy may be confirmed by your GP. An initial consultation with your GP will involve a detailed history of your symptoms in order to identify the underlying condition. Your GP may refer you to a neurologist who will carry out a number of tests to determine the underlying cause of neuropathy and rule out other conditions. Tests may include blood test, CT scan, MRI scan and nerve conduction test in order to confirm a diagnosis.
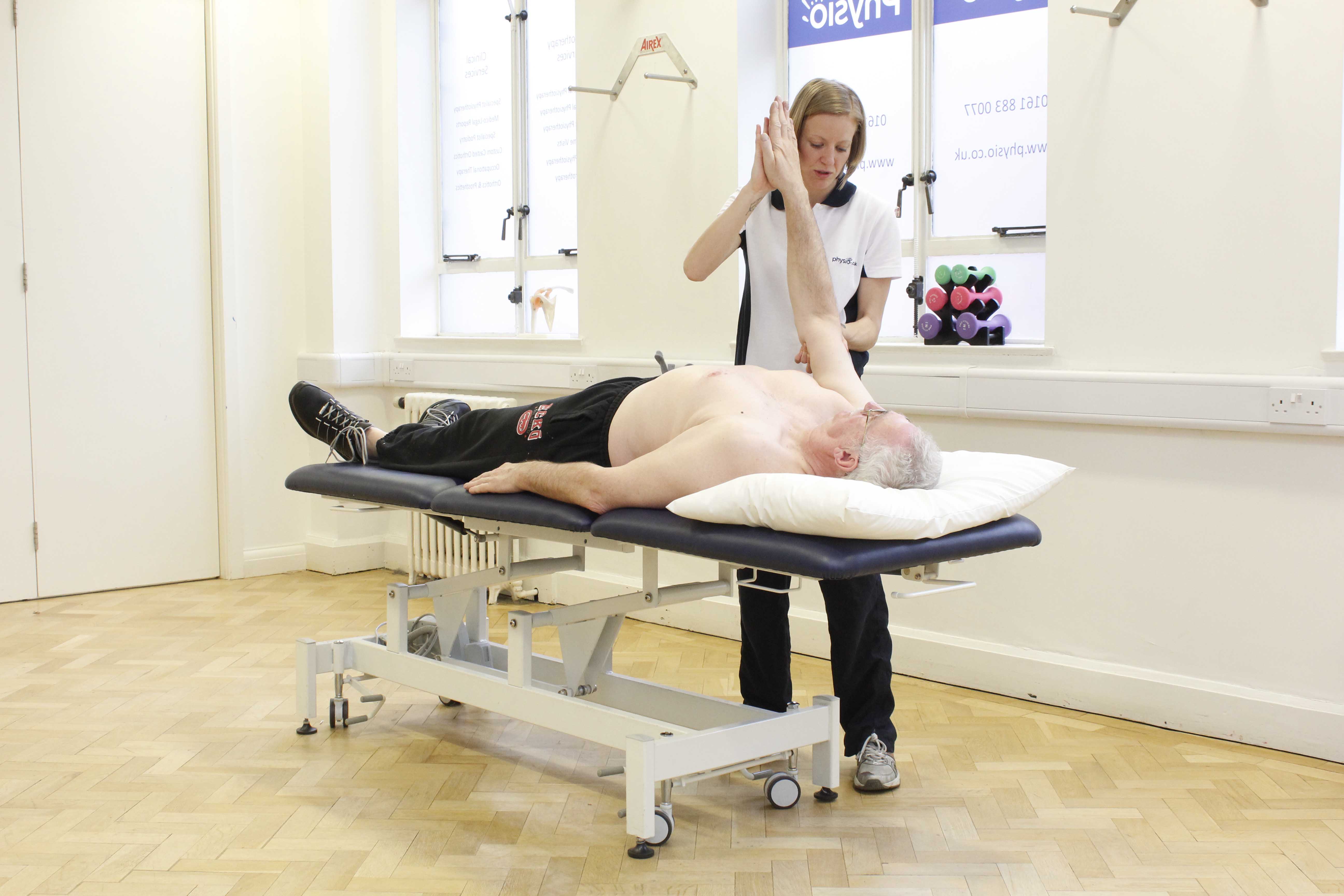 Above: functional hand exercises to address loss of sensation and fine motor control in limb peripheries
Above: functional hand exercises to address loss of sensation and fine motor control in limb peripheriesWhat causes a peripheral neuropathy?
There are many different causes of peripheral neuropathy, with different symptoms, requiring different physiotherapy treatment. Causes of peripheral nerve injury may include:
- Autoimmune diseases - such as Guillian-Barre syndrome. This occurs when the immune system attacks the myelin (protective sheath) that surround the nerve fibres disrupting signals travelling along these fibres resulting in a loss of muscle strength, difficulty walking and abnormal sensation
- Cancer – itself may cause nerve damage or the treatment for cancer such as chemotherapy can cause nerve pain and nerve damage.
- Compression/trauma – may result in nerve damage and nerve pain. This may include pinched nerves in the neck, crush injuries, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Diabetes - Peripheral nerve damage occurs in approx 50% of people with diabetes. The risk of developing diabetic neuropathy increases with age and nerve damage can occur throughout the body. Some people with nerve damage have no symptoms. Others may have symptoms such as pain, tingling, or numbness in the hands, arms, feet, and legs. Uncontrolled high blood glucose levels are a contributing factor to nerve damage.
- Drug side effects and toxic substances – alcohol use and medications, such as chemotherapies for cancer and certain drugs used to treat HIV can cause nerve damage.
- Nutritional deficiencies - such as vitamins B6 and B12, may produce symptoms of nerve pain and nerve damage, including weakness or burning sensations.
- Infectious disease - Lyme disease, the herpes viruses, HIV, and hepatitis C can damage nerves.
- Inherited disease - diseases that are genetically transmitted or passed on through the family can result in peripheral neuropathy. These include Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Dejerine-Sottas Disease, Congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy, Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy and Friedreich's ataxia.
What are the effects/symptoms of a peripheral nerve injury?
The symptoms of a peripheral injury will depend on the type of nerves affected. Symptoms may include:
- Muscle weakness, wasting and muscle twitches
- Loss of sensation including numbness and tingling, decreased proprioception (balance) loss of coordination and ability to detect pain
- Burning, stabbing or shooting pain (neuropathic pain)
- Problems with autonomic function including fainting, dizziness and bladder and bowel function.
Physiotherapy for peripheral neuropathy
Physiotherapy treatment will improve your mobility and balance as well as your ability with daily tasks important to you. Treatment will depend on your individual symptoms but may involve:
- Individualised exercise program to strengthen muscles and improve fitness levels
- Passive movement of muscles and joints
- Weight bearing through a joint
- Balance training to reduce the risk of falling
- Gait re-education to facilitate mobility and promote independence
- Soft tissue massage
- Task-specific sessions using graded discrimination tasks, attentive exploration of objects without vision and feedback.
- Mirror imaging to stimulate nerve pathways
- Pain management. Hydrotherapy treatment relaxes muscle and increases circulation. This type of treatment can also reduce pain and will enable you to maximise your mobility within the water.
- Advice and support about diet
- Advice about walking aids, orthotics, callipers and wheelchairs.
- Improving safety with everyday tasks
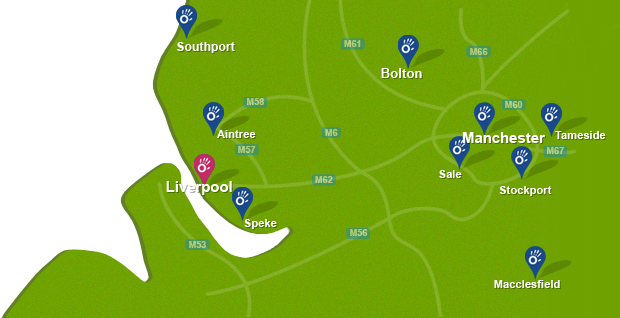
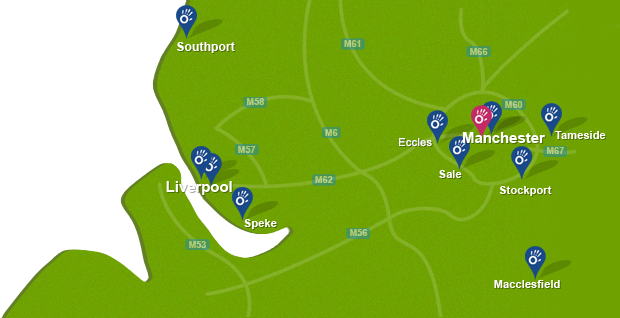
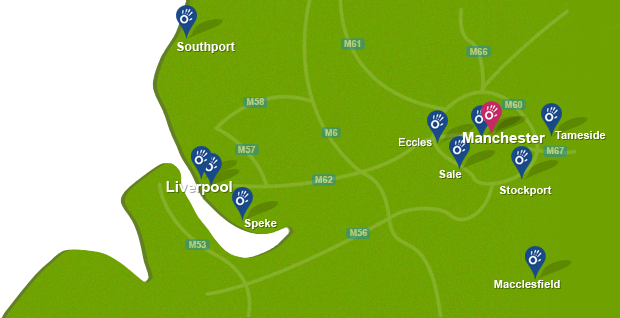
To book an appointment call 0330 088 7800, book online or alternatively request a free phone consultation.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800