What is paediatric spasticity?
Spasticity in children is involuntary, velocity-dependent, increased muscle tone that causes resistance to movement. Spasticity can affect any part of the body. It can make everyday activities and functioning extremely difficult.
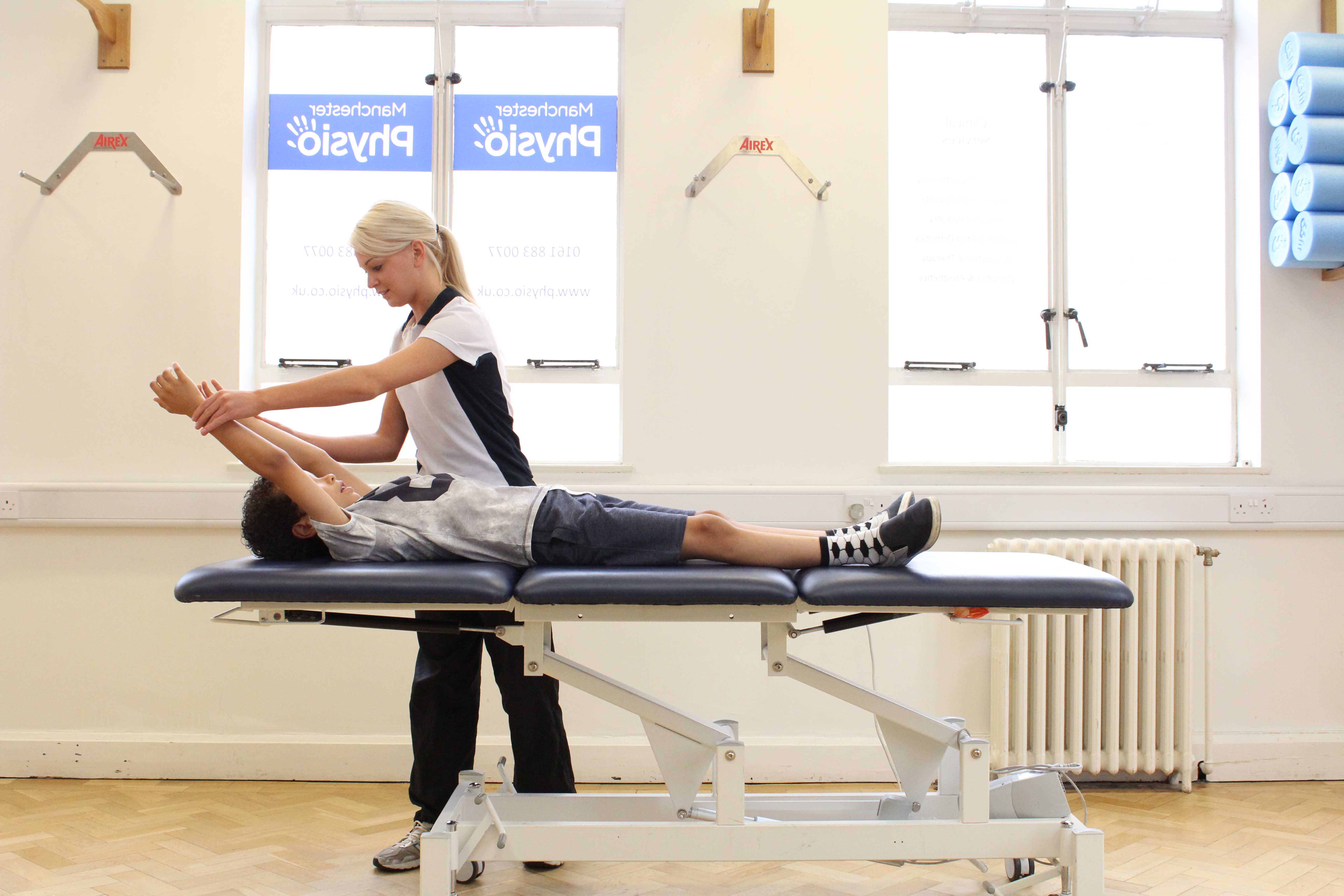 Above: Our physiotherapist supporting a child suffering with spasticity in his upper limb
Above: Our physiotherapist supporting a child suffering with spasticity in his upper limbWhat causes spasticity in children?
Spasticity in children may be caused secondary to a disorder or trauma such as:
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Traumatic Brain injury (TBI)
- Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
What are the symptoms of spasticity in children?
Symptoms of spasticity include:
- Involuntary “scissoring” (crossing of the legs)
- Involuntary spasms (contraction and relaxation of muscles)
- Increased resistance to movement of certain muscle groups
- Exaggerated deep tendon reflexes
- Prolonged muscle contractions (dystyonia)
- Abnormal posture or positioning of the arm, shoulder, wrist or finger
- Repetitive, rapid jerky movements (clonus)
- Increased muscle stretch reflexes
How can physiotherapy help children with spasticity?
Physiotherapy treatments can help children with spasticity improve everyday functioning and independence, reduce pain, and improve quality of life. Treatments commonly include:
- Stretching
- Strengthening
- Orthotics
- Positioning
- Hydrotherapy
- Biofeedback
- Botulinum Toxin injections
Summary
Spasticity in children is an involuntary, velocity-dependent increase in muscle tone, which causes increased resistance to movement. It is caused secondary to disorders such as Cerebral Palsy, Spinal Cord Injuries, or Traumatic Brain Injuries. Symptoms of spasticity include involuntary “scissoring” of the legs, involuntary spasms and prolonged muscle contractions to name a few. Physiotherapists at Physio.co.uk understand how debilitating Spasticity can be for children and are here to help. Through a variety of treatments including stretching, positioning, strengthening and hydrotherapy, our physiotherapists can help your child increase range of movement, reduce pain, and improve overall function and quality of life.
To book an appointment or for more information regarding paediatric spasticity contact us or call 0330 088 7800.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800