What is a groin strain?
A groin strain (or adductor muscle strain) is a tear in one of the muscles on the inside of the thigh. Physiotherapy is important for the treatment of a groin strain.
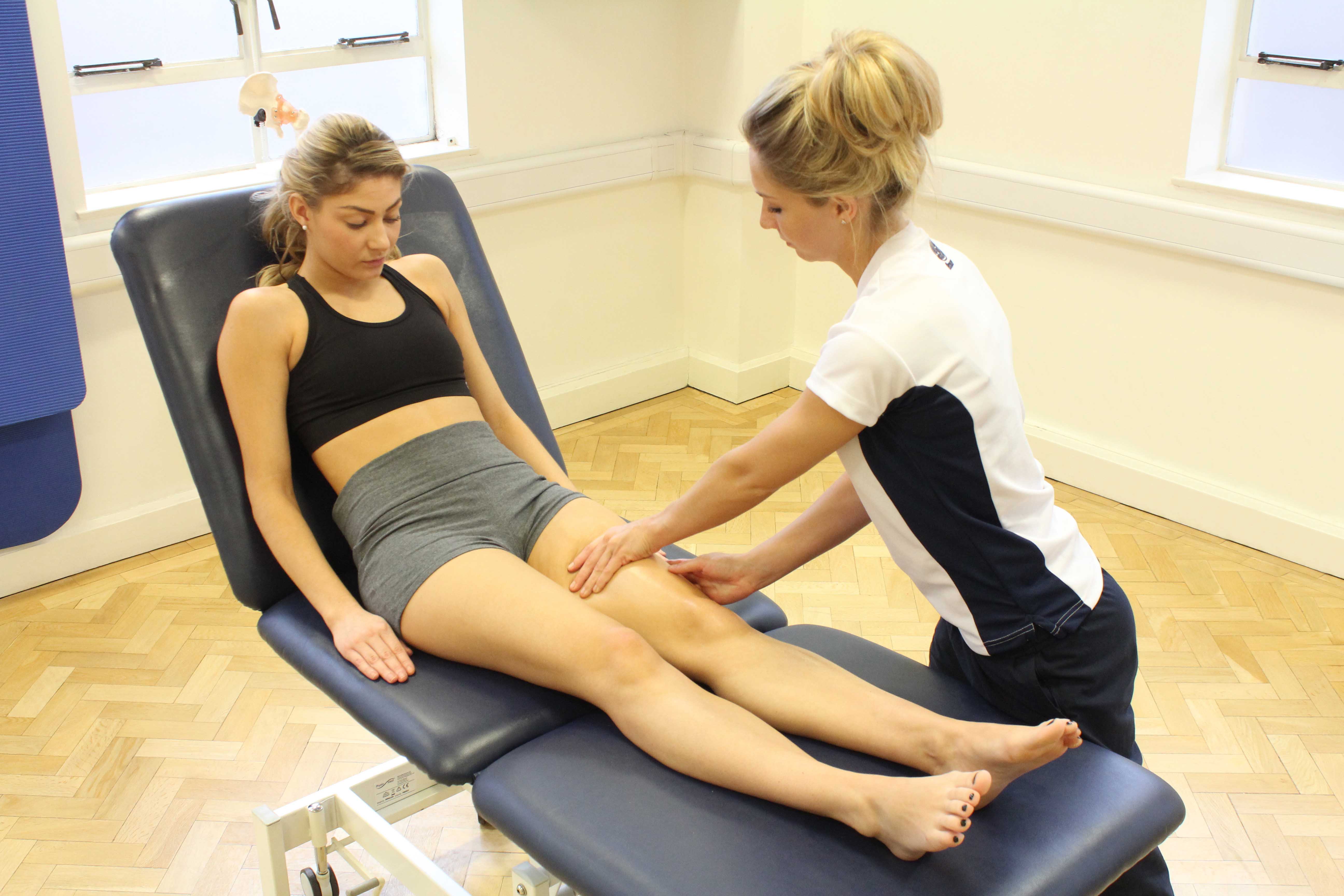 Above: Soft tissue massage of the muscles and connective tissues around the groin by an experienced therapist
Above: Soft tissue massage of the muscles and connective tissues around the groin by an experienced therapistHow does a groin strain happen?
A groin strain is usually caused by overstretching and/or powerful contraction of the muscles in the groin. This commonly occurs if you change direction sharply when running.
What are the symptoms of a groin strain?
Sudden pain is felt along the inside of the thigh or the groin region when a groin muscle is torn. You may also experience a ‘tearing’ sensation. In minor tears, the pain often worsens significantly following participation as bleeding and swelling occurs around the injured muscle. Other symptoms include:
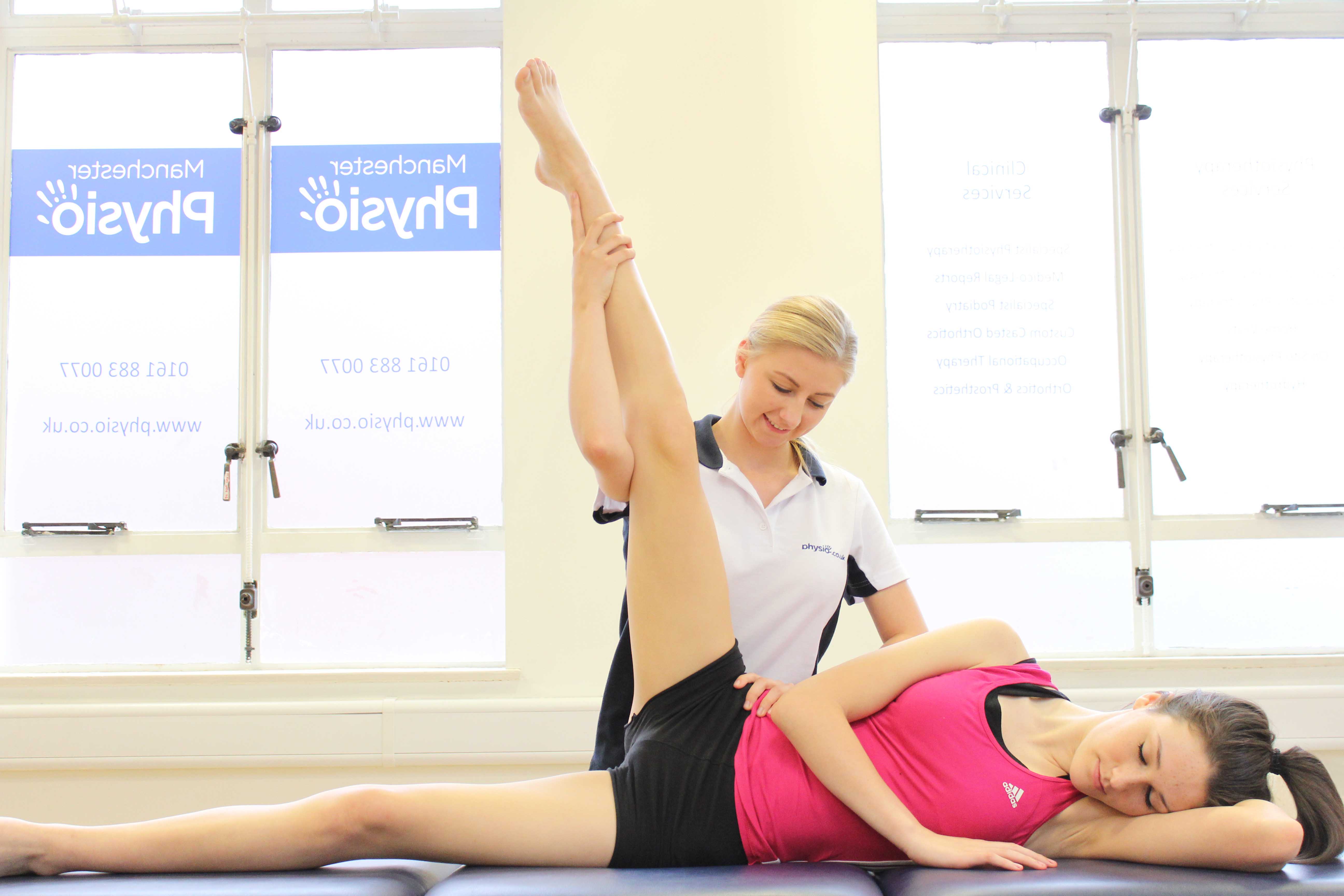 Above: Passive stretch of the muscles and connective tissues of the hip and groin by specialist therapist
Above: Passive stretch of the muscles and connective tissues of the hip and groin by specialist therapistWhat should I do if I have a strained a groin muscle?
For the first 24 – 48 hours the RICE regime should be followed (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation).The RICE regime helps reduce bleeding and swelling in and around the muscle and, therefore limits the amount of damage to it. Rest involves limiting the amount of weight you put through the injured leg. With a severe tear crutches may be required. Ice should be applied to the injured site, using a bag of frozen peas or crushed ice wrapped in a damp cloth, for 15–20 minutes every 1–2 hours. Compression should be firm but not so tight as to cause pain. It can be applied using an elasticated bandage. Finally, the leg should be elevated comfortably on a chair or pillows, preferably so that the injured site is above the level of the heart. You should arrange an initial assessment with a physiotherapist as soon as possible following your injury. The RICE regime should be continued until you see your physiotherapist.
Physiotherapy treatment for a groin muscle strain.
Physiotherapy is very important in the effective treatment of a groin strain. Initially, your physiotherapist can determine the exact tissue/s damaged, the extent of the damage and determine a time scale for complete recovery. Your physiotherapist may use a number of treatment techniques to reduce your pain and swelling, and accelerate the healing of the damaged structures. These techniques include:
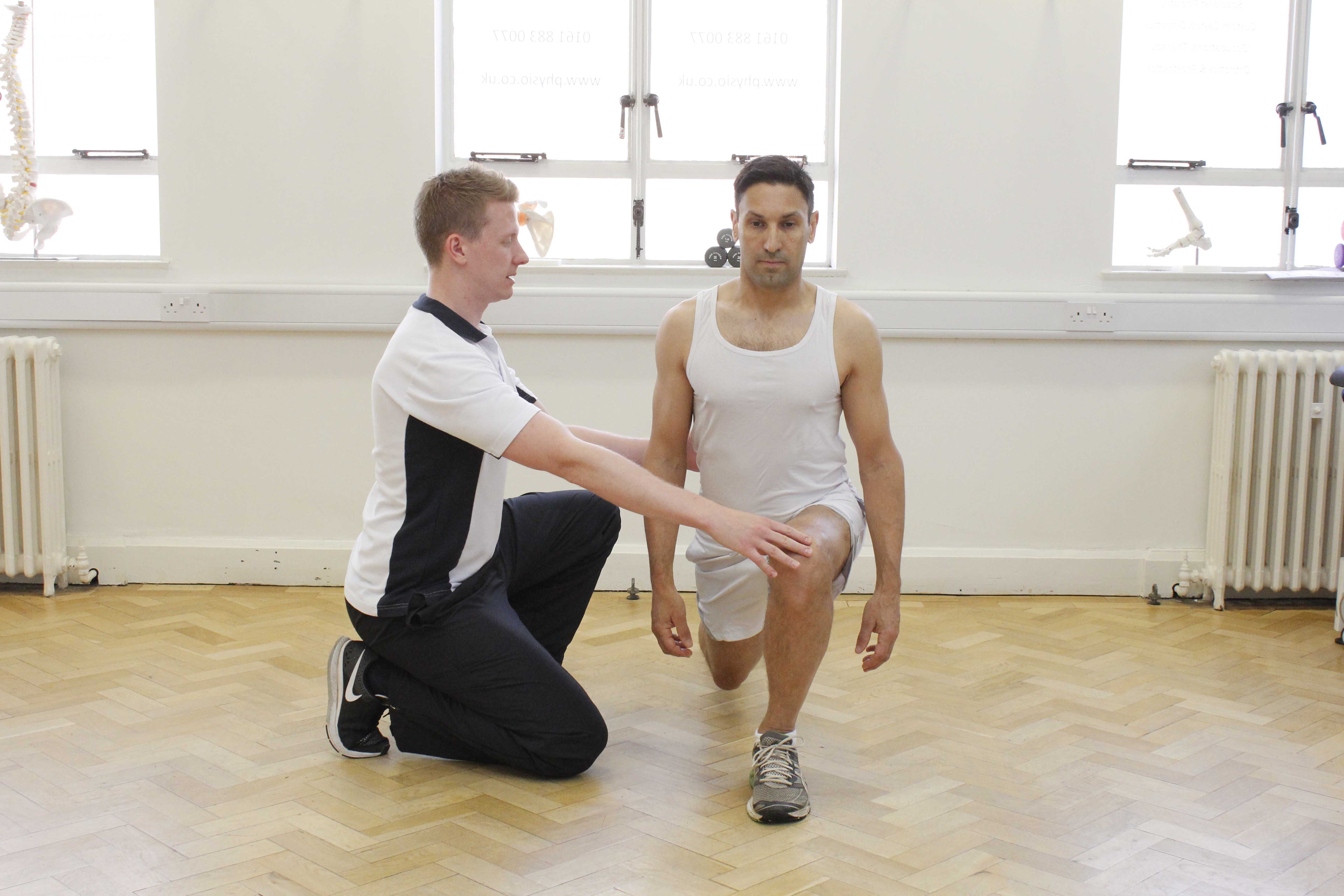 Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapist
Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapistWhat shouldn’t I do if I have strained a groin muscle?
In the first few days following your injury, you should avoid hot showers, groin stretching, heat rubs, massage, the consumption of alcohol and excessive activity. This is because these activities can increase blood flow to the area and, therefore, prolong muscle bleeding causing increased pain and an extended recovery.
Could there be any long-term effects from an adductor muscle strain?
The majority of groin strains heal without complication within weeks. However, depending on the severity of the injury and amount of damage, some injuries can cause longer-term effects. When a significant groin strain occurs, a number of other structures in the groin may also be injured. Injury to these structures can delay recovery. Recovery can also be delayed if the injury is not managed correctly. Incorrect management can cause tight, weak muscles in the groin that are more likely to be reinjured in the future.
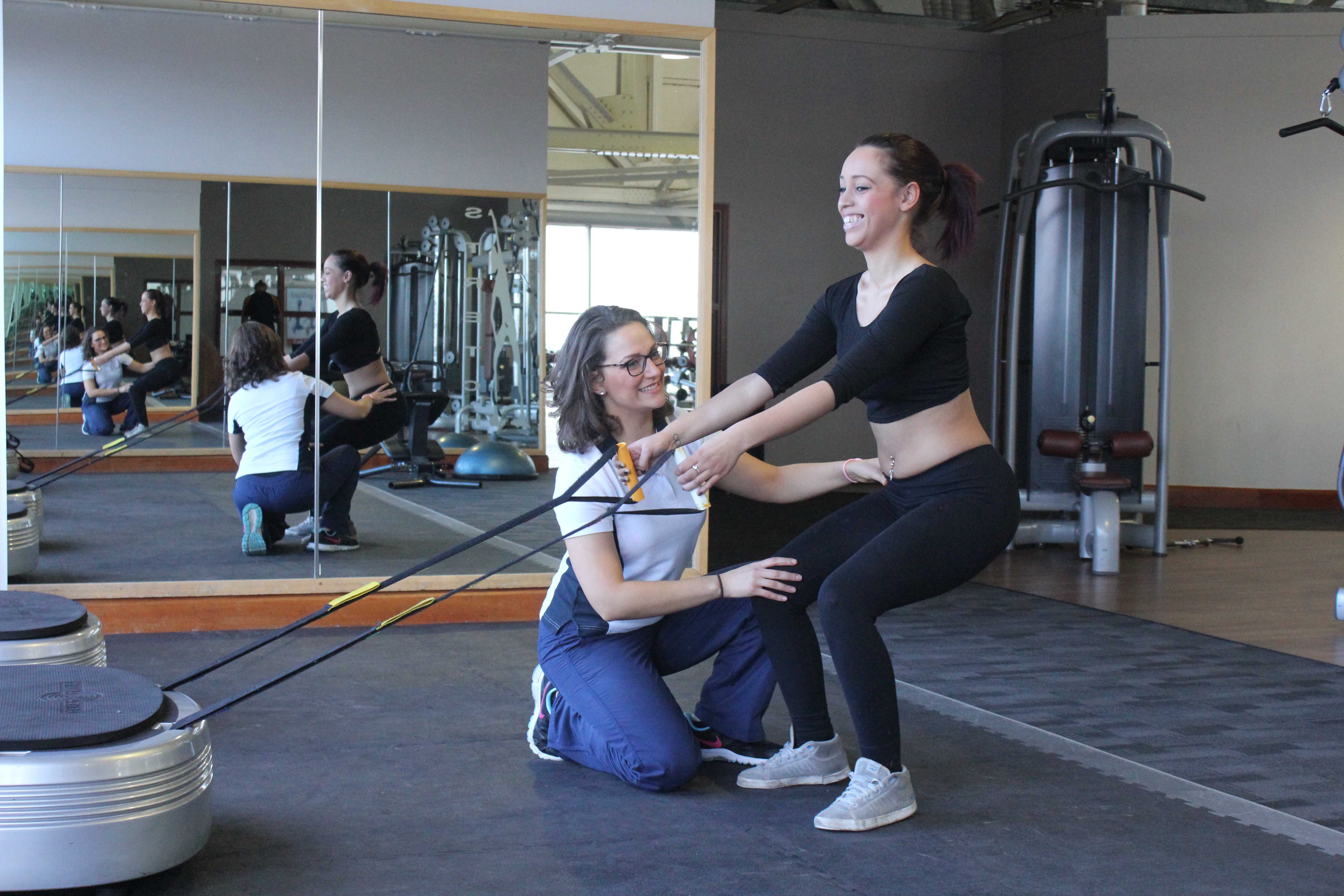 Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapist
Above: Progressive strengthening hip exercises supervised by experienced therapistTo arrange a physiotherapy assessment call Physio.co.uk on 0330 088 7800 or book online.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800